The modern construction industry is changing rapidly, and Building Information Modelling (BIM) is leading the way. In the UK and worldwide, BIM has become more than just a trend—it’s a new way of designing, managing, collaborating, and delivering projects.
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a collaborative digital platform that brings architects, engineers, contractors, and clients together. It enables seamless communication and teamwork throughout a project’s lifecycle.
Whether you’re new to BIM or wish to master its advanced capabilities, this article will equip you with the essential strategies to transform your projects. You’ll learn how BIM influences project lifecycle management, promotes environmental sustainability, and opens up exciting opportunities for the construction industry. Let’s start!
Introduction to BIM and Its Role in the Construction Industry
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a digital tool used in the design, construction, & management of buildings and infrastructure. It involves creating a detailed 3D model that represents a project’s physical and functional aspects.
Unlike traditional methods that depend on 2D drawings and isolated workflows, BIM connects all project teams in a unified digital space. This collaborative approach allows architects, engineers, contractors, and owners to work together seamlessly.
BIM is more than just generating 3D models. It includes detailed information about materials, sizes, systems, schedules, and how everything works together. Each part of the construction project is represented as a smart object with built-in information.
BIM enhances project efficiency by optimising resource allocation and reducing time delays. It supports the entire building lifecycle, from design and construction to maintenance and operation, making long-term performance management easier.
BIM also promotes better sustainability by enabling energy analysis and other environmental assessments. Overall, it streamlines construction, reduces risks, and leads to higher-quality outcomes.
Now that we’ve discussed the role of BIM let’s dive deeper into how it transforms every phase of your project workflow.
BIM in Project Lifecycle Management

Effective project management is crucial for completing construction projects on time and within budget. As projects become more complex, traditional methods often fail, causing delays, extra costs, and inefficiencies. Building Information Modelling (BIM) improves how projects are planned, carried out, and managed. Let’s dive deep and find out how BIM adds value at various stages of the project lifecycle.
1. Planning through Detailed Digital Models
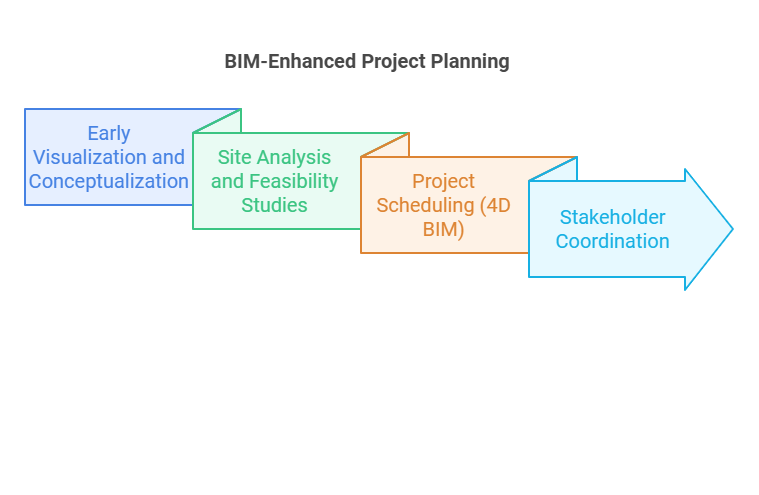
The planning phase lays the base for a successful construction project. BIM creates detailed digital models that help teams visualise the entire project before construction begins.
- Early Visualisation and Conceptualisation – BIM allows stakeholders to view the project in 3D and provides a realistic design representation. It helps with better decision-making as stakeholders can review the design, make adjustments, and ensure alignment with project goals.
- Site Analysis and Feasibility Studies – BIM helps project teams assess site conditions, environmental factors, and potential challenges before finalising the design. By integrating geographic and environmental data, BIM models simulate site conditions, help identify issues early, and avoid costly changes later.
- Project Scheduling (4D BIM) – BIM can create detailed schedules linked to the digital model. This 4D timeline simulation shows the project timeline within the construction process and helps planners optimise resource allocation and ensure the project stays on schedule.
- Stakeholder Coordination – BIM enhances stakeholder coordination during the planning stage by having all project data in one centralised digital model. The team can collaborate on the same platform, ensuring everyone works with the same updated information. It reduces miscommunication and minimises delays.
3. Design Efficiencies and Logistics Management
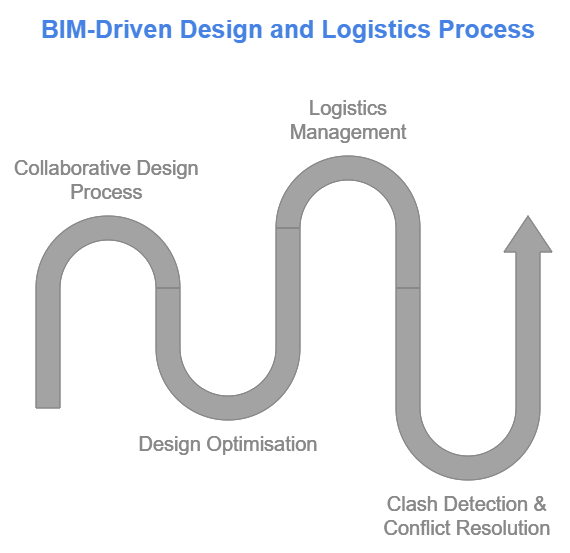
BIM significantly boosts the efficiency of the design phase by promoting collaboration, improving design accuracy, and streamlining logistics management.
- Collaborative Design Process – BIM allows quick, real-time design iterations to be shared with all parties. It ensures alignment and reduces errors, conflicts, or misalignments between systems.
- Design Optimisation – BIM helps optimise building performance by modelling and simulating various design options. Designers can use energy analysis, daylight simulations, and material assessments to assess how choices affect efficiency and sustainability.
- Logistics Management – BIM streamlines logistics during the design phase by planning on-site material procurement, delivery, and storage. It reduces material waste and delivery delays.
- Clash Detection & Conflict Resolution – BIM’s clash detection tools help identify and resolve conflicts between systems early in the design phase. For instance, if a structural column clashes with a door opening, these issues can be fixed digitally before construction, avoiding costly and time-consuming delays and onsite rework.
3. Construction Phase Support with Digital Integration
BIM links the design model with construction activities during construction, provides real-time updates, and supports project execution. This integration optimises workflows and minimises potential issues during construction.
- Real-Time Information and Communication – BIM is a central hub for all project data, ensuring stakeholders can access the latest designs, schedules, and change orders. This real-time access helps teams make informed decisions on-site and communicate effectively.
- Construction Sequencing and Scheduling (4D BIM) – BIM simulates the construction sequence (4D BIM), showing how each project phase unfolds. It helps construction managers plan, allocate resources efficiently, and identify potential delays before they occur.
- Quantity Takeoffs and Material Management (5D BIM) – BIM automatically generates detailed quantity takeoffs from the digital model. It reduces the risk of shortages or over-ordering, leading to cost savings and less material wastage.
- Quality Control and Issue Resolution – BIM supports continuous quality monitoring during construction. Teams can document issues or deviations from the design, and discrepancies are flagged and tracked within the model. It helps ensure the project stays on target and reduces the need for corrections after construction.
- Site Coordination and Logistics – BIM integrates with construction logistics to plan site layout, delivery routes, equipment placement, and temporary structures. Visualising these elements in the model helps project managers optimise space and ensure the smooth movement of materials, personnel, and equipment on-site.
4. Ongoing Operations and Maintenance Support
BIM is crucial for the long-term operation and maintenance of the building. It becomes a valuable resource for facility management throughout the building’s lifecycle.
- As-Built Models for Facility Management – After construction, the BIM model gets updated to reflect the as-built condition of the building, providing an accurate digital record of the finished project. This model becomes an essential tool for facility managers, offering detailed information on the building’s systems and components.
- Maintenance Scheduling and Asset Management – BIM tracks the life cycle of building components, including maintenance schedules, warranties, and replacement timelines. It allows facility managers to plan preventive maintenance more effectively, extend asset lifespan, and prevent unexpected breakdowns.
- Energy Management and Sustainability – The energy performance data embedded in the BIM model helps to monitor and optimise the building’s energy use. Facility managers conduct energy audits, track consumption, and implement sustainability measures to improve efficiency.
- Space Management and Modifications – The BIM model supports modifications or space reconfigurations as building needs change. Facility managers use the model to evaluate potential changes and ensure redesigns or repurposes of space are done efficiently.
Are you looking for 3ds Max-based solutions? BIM ASSOCIATES helps with the 3d modelling of your object, furniture, building, and landscape and helps you create a scenic render and video.
So far, we have discussed different stages of the project’s lifecycle and saw how BIM adds value at each stage. Let’s learn how BIM sets the groundwork for standardizing and unifying construction practices.
BIM Standards and Interoperability
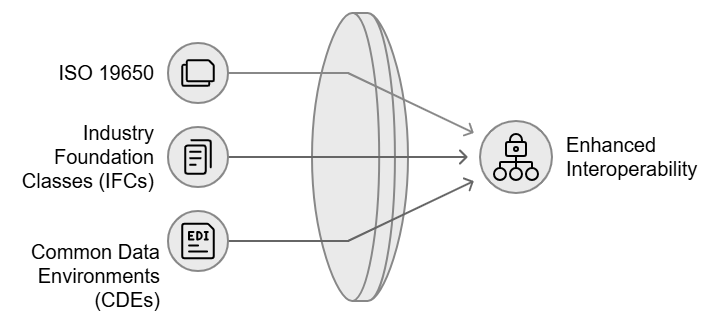
BIM standards and interoperability are essential for ensuring that everyone in the construction industry works consistently and efficiently. As BIM technology becomes more common, having clear guidelines and rules helps keep things running smoothly. Here’s a deeper look at these key aspects.
Adoption of Common Data Environments (CDEs)
A Common Data Environment is a centralised digital repository where all project data, documents, and information are stored, shared, and managed throughout the project lifecycle. Ensuring the efficient use of BIM models and providing all stakeholders access to the most current information is essential.
CDEs offer a single source of truth for all project data, including 3D models, 2D drawings, specifications, schedules, and communications. This approach reduces errors caused by conflicting or outdated data and ensures team consistency.
With a CDE, all project participants can access and contribute to the data anytime, anywhere. It enhances collaboration and speeds up decision-making, as changes made by one team are visible to others. It also increases transparency and accountability, as each change is tracked and documented.
In addition, CDEs provide version control and ensure that the latest model or document is always available while maintaining a record of past versions. It is beneficial for managing complex projects with many revisions, allowing teams to revert to earlier versions if needed.
CDEs also allow project owners to control access to sensitive data. This security protects the integrity of project data and safeguards intellectual property. Adopting a CDE enables project teams to work more efficiently, minimise miscommunication, and maintain better control over project data, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes.
ISO 19650 and Industry Foundation Classes (IFCs)
ISO 19650 and Industry Foundation Classes (IFCs) are two key standards that outline how BIM data should be structured, managed, and exchanged.
ISO 19650 is an international standard for managing BIM throughout a building’s life cycle. It provides clear guidelines for organising and handling information to ensure it is accurate, easy to access, and reliable. ISO 19650 is split into different parts, with the key ones being ISO 19650-1, ISO 19650-2, and ISO 19650-3.
ISO 19650-1 focuses on managing information during the planning, design, and construction stages. On the other hand, ISO 19650-2 deals with managing information during the construction phase. ISO 19650-3 covers how BIM should be used for managing the building after construction, including operations and maintenance.
The goal of ISO 19650 is to create a consistent way of managing information in BIM. It ensures clear communication and alignment across international construction projects. In addition, it helps teams understand information needs, responsibilities, and deadlines, leading to smoother processes and fewer mistakes.
On the other hand, Industry Foundation Classes (IFCs) are an open and non-proprietary data format created by the BuildingSMART alliance. They allow different BIM software systems to work together by providing a standardised way to share and exchange construction data. IFC is an open standard that ensures data is easily shared across different platforms & disciplines.
It supports various construction elements, such as architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing components. This makes them suitable for use in various projects and construction fields.
ISO 19650 and IFCs lay the groundwork for standardised and interoperable BIM practices. They help improve efficiency, ensure consistency, and encourage collaboration throughout a project’s lifecycle.
Now that you know about BIM standards and interoperability, let’s move ahead and learn about BIM technologies and tools.
Cutting-Edge BIM Technologies and Tools
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a complex process that combines various advanced technologies and tools. These tools are crucial in changing how construction projects are designed, built, and maintained. So, let us look at the key BIM technologies and tools shaping the construction industry’s future.
Use of 3D Models and Data-rich BIM Objects
One of the key features of BIM is the use of 3D models, which help visualise, plan, and communicate the design of a construction project. The 3D model helps identify design issues early, improves communication among team members, and allows clients to understand the project before construction begins.
Each object in a BIM model is more than just a geometric shape. These objects include detailed information about the physical and functional characteristics of the building components, like materials, dimensions, quantities, and manufacturer details. In addition, performance metrics such as thermal efficiency, structural integrity, and maintenance needs are also found in these objects.
One of the major benefits of 3D BIM models is their ability to detect clashes or conflicts between different building systems. The detailed 3D models are a shared resource that all project stakeholders can access and update.
Integration of Advanced Technologies like IoT & AI
BIM integrates more with advanced technologies like the Internet of Things & Artificial Intelligence. These technologies enhance the capabilities of BIM, providing more innovative, dynamic solutions for managing construction projects and their ongoing operations.
In BIM, IoT devices can be integrated into a building during construction and used throughout its lifecycle. In addition, sensors embedded in a building’s infrastructure, such as glass facade sensors, room occupancy sensors, HVAC systems, lighting, and security, can provide real-time data to the BIM model. This data allows building managers to monitor energy usage, occupancy, air quality, temperature, and other performance metrics.
IoT devices can also monitor construction sites in real time, tracking variables like equipment location, material inventory, and worker productivity. This data can be integrated into the BIM model to provide live updates, optimise workflows, and enhance safety on site.
On the other hand, AI algorithms analyse historical data to provide predictive insights, such as identifying potential delays or cost overruns. AI can also automatically generate design options based on specific parameters. It can help architects and engineers quickly explore configurations or optimise building performance.
Digital Construction Methods and Prefabrication
Digital construction methods use digital tools and technologies to plan, design, and manage construction activities. Virtual Reality & Augmented Reality can be integrated with BIM models to help project teams visualise the construction process in immersive 3D environments.
VR can be used for design validation, while AR can spread digital information in physical spaces, providing on-site workers with real-time guidance and information. BIM models can also be integrated with robotic systems to automate repetitive tasks, improve productivity, and reduce human error.
On the other hand, prefabrication and modular construction assemble building components off-site in controlled factory environments. After that, it gets transported to the construction site for final assembly.
BIM is used to streamline the supply chain for prefabricated components. It ensures that materials are delivered quickly and those parts are fabricated to precise specifications. It also reduces the risk of delays and waste associated with traditional construction methods.
Prefabricated components are typically faster to assemble than traditional site-built elements. This leads to quicker project completion and fewer disruptions caused by weather or other factors. Furthermore, prefabrication can improve quality control, as components are built in controlled environments rather than exposed to the elements.
If you want to implement BIM architecture in your projects, BIM ASSOCIATES offers expert services to streamline your design, collaboration, and construction process.
Now, you’re aware of BIM technology and tools, so let’s discuss how BIM positively impacts the environment.
How BIM Enhances Sustainability and Reduces Environmental Impact in Construction?
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is gaining recognition for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and addressing the environmental and sustainability challenges in the construction industry. Here’s how:
- Reduce Embodied Carbon – Embodied carbon refers to the greenhouse gas emissions associated with producing, transporting, and assembly of building materials and components. BIM reduces embodied carbon by helping design teams make sustainable material choices, minimize clashes during the actual construction phase, reduce material waste, and optimise the entire building lifecycle.
- Optimise Material Selection – BIM allows for detailed modelling of the building’s structure, systems, and materials. Designers use BIM to evaluate the environmental impact of various materials based on their embodied carbon content. It reduces material wastage by providing precise calculations for quantities, ensuring that materials are used efficiently. This also helps in better cost planning of the building process.
- Designing for Maintenance, Demolition and Reuse – Stakeholders can plan to maintain, reuse, or recycle building materials eventually. The BIM Model will give the necessary base to the task. It will help significantly reduce the carbon impact at the end of a building’s life.
- Sustainability Analytics and Reporting – BIM tools generate sustainability reports that offer insights into the building’s environmental performance. These reports help track compliance with green building standards, identify areas for improvement, and communicate the project’s sustainability achievements.
Now that you know the impact of BIM on the environment, let’s move ahead and learn how BIM can impact everyone’s life. BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.

Benefits of BIM in Construction

Building Information Modelling (BIM) has revolutionised the construction industry by streamlining processes, enhancing collaboration, and improving project outcomes. Let us look at the benefits of BIM.
Enhanced Collaboration Among Stakeholders
BIM offers a shared digital model that everyone involved in the project can access & update in real time. Whether the architect updates the design, the engineer adjusts specifications, or the contractor reviews constructability, BIM ensures everyone can access the latest information.
In addition, visualising the project in 3D and simulating different situations allows the stakeholders to review and improve design choices together. The visualisation tools, like 3D models and virtual walkthroughs, help all team members understand and discuss the project.
Moreover, BIM also spots issues between systems early in the design process so teams can fix problems before construction begins.
Efficiency Improvements and Cost Reduction
According to the ResearchGate Case Study, the results showed that BIM could cut time by 50% faster and reduce costs by 52.36%.
BIM combines cost data with the 3D model and makes accurate cost estimates throughout the project. It automatically calculates material quantities, labour, and other costs. It helps prevent budget overruns and keeps the project on track financially.
In addition, BIM allows all stakeholders to work together using a centralised model. As a result, the design changes are instantly reflected across the team. It eliminates delays from communication gaps or outdated drawings. Also, testing different design options digitally reduces the need for physical mockups and revisions.
Furthermore, BIM’s clash detection feature automatically identifies and resolves conflicts between systems and components. Finding clashes early in the design phase helps avoid costly changes and rework during construction.
Better Safety Through Risk Identification and Management
Safety is a major concern in the construction industry, with risks of accidents, injuries, and even fatalities. BIM allows project teams to analyse potential hazards and evaluate safety risks in a virtual environment. It identifies areas where safety measures need improvement.
In addition, BIM allows workers to explore the site virtually before working on it. Virtual walkthroughs and simulations help workers identify hazards and understand safety protocols. Moreover, BIM’s real-time data integration allows teams to track safety metrics throughout the construction process.
Also, explore the GFC BIM Model Case Study to see innovation in action! It reduced design conflicts & gave a better hand in construction & BOQ.
Now that you know the benefits of BIM, it’s crucial to understand how this technology shapes the future of the UK construction industry.
Future Prospects of BIM in Construction
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is already transforming the construction industry, but its future holds even greater potential, especially from a global perspective. While BIM is already widely used in developed countries, its adoption in emerging markets like the UK, the USA, Australia, and Russia is rapidly growing.
Let’s discuss how it is revolutionising the UK construction industry.
Sustainability and Green Building
Sustainability is a top priority in the UK. The construction industry is pressured to cut carbon emissions to meet net-zero targets by 2050.
BIM plays a big role by allowing designers to analyse energy use, materials, and environmental impact. Its tools, like energy modelling and carbon tracking, ensure projects like BREEAM and Passivhaus meet green building standards.
Digital Twin Technology
Digital Twin technology is one of the most exciting developments for BIM in the UK. It creates a virtual copy of a real building or infrastructure. Adding real-time data to these digital models helps make smarter decisions, predict maintenance needs, and manage buildings more efficiently.
The UK construction industry is already using Digital Twins for infrastructure projects, and this trend is growing to include buildings. It will lead to long-term savings and better building management.
Collaboration and Interoperability
The UK construction industry focuses on improving teamwork and ensuring different teams can easily share information. BIM tools and standards like IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) help ensure data can be shared smoothly across different software, reducing mistakes and improving coordination. As projects become more complex, seamless teamwork becomes a major advantage, especially with the growing use of off-site construction and modular building.
Skills and Training
BIM adoption needs a skilled workforce. The demand for BIM professionals is growing, and training programmes and certifications are helping prepare workers for this shift. The UK government is also focusing on developing digital skills and creating a workforce ready for the challenges of a more digital construction industry.
Automation and Prefabrication
BIM’s role in supporting automation and prefabrication is growing. By combining BIM with advanced manufacturing and robotics, UK construction companies can produce high-quality building parts off-site, reducing waste, construction time, and costs. This trend supports the UK’s focus on Modern Methods of Construction (MMC), which aims to address housing shortages and make buildings more efficient.
The future of BIM in the UK construction sector looks set to drive innovation, sustainability, and efficiency. As we have discussed everything about BIM’s impact on the construction industry, let’s wrap up with a quick summary.
Conclusion
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is changing how construction works in the UK and worldwide. It is making projects more efficient, collaborative, and sustainable. BIM helps improve every project stage, from planning and design to construction. The tool makes it easy for everyone involved in the project to share information and work together.
With the latest BIM tools, construction teams can complete projects more accurately, on time, and with less waste while creating energy-efficient designs. BIM lowers costs, reduces mistakes, and improves the overall quality of buildings.
The future of BIM is even more exciting, with new technologies like digital twins, automation, and prefabrication. As BIM adoption grows in the construction industry, emphasising training and digital skills will prepare workers to benefit fully from these innovations.
BIM is increasingly being utilised for smaller projects alongside larger ones. It is shaping the future of construction in the UK by making it more efficient, sustainable, and collaborative.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Architecture and Structure. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What does a BIM modeller do?
A BIM Modeller creates and manages 3D digital models of buildings and structures. These models include detailed information about the building’s design, construction, and use, helping throughout its entire lifecycle.
- Are CAD and BIM the same?
No, they are not the same. CAD is used to create 2D or 3D drawings using lines, while BIM lets you build a virtual model of a building using smart objects.
- What is the BIM tool?
BIM is a smart, 3D model-based tool that digitally represents a building’s physical and functional features.

