BIM has revolutionised the modern construction and design industry by offering a collaborative platform that enhances project management efficiency and delivers tangible benefits. It reduces project planning time by up to 20% and material costs by approximately 15%. These advantages underscore the transformative potential of BIM when implemented effectively.
However, achieving these benefits requires more than just adopting advanced technology—it demands a structured approach, clear strategies, and unwavering stakeholder commitment. Success depends on addressing every step, from thorough planning and team training to selecting the right tools and refining workflows for seamless integration and optimal results.
This article will guide you through effective BIM implementation strategies for your projects, enabling you to utilise BIM’s full potential. With these insights, you can achieve sustainable, efficient, and high-quality outcomes.
Understanding BIM Implementation Plan & its Types
A BIM Implementation Plan is a detailed strategy to guide the adoption and management of Building Information Modelling (BIM) within a project or organisation. This plan ensures all stakeholders agree on objectives, roles, and deliverables. Promoting collaboration and clear communication helps reduce risks and enhance project efficiency.
BIM implementation involves systematically integrating BIM practices into project workflows and organisational operations. A well-crafted implementation plan provides a clear roadmap for incorporating BIM, ensuring a smooth transition and long-term success.
The success of BIM adoption largely depends on tailoring the implementation strategy to align with specific project goals and organisational objectives. Different types of BIM implementation plans address the unique needs of each project or business to tackle challenges effectively.
Types of BIM Implementation Plans
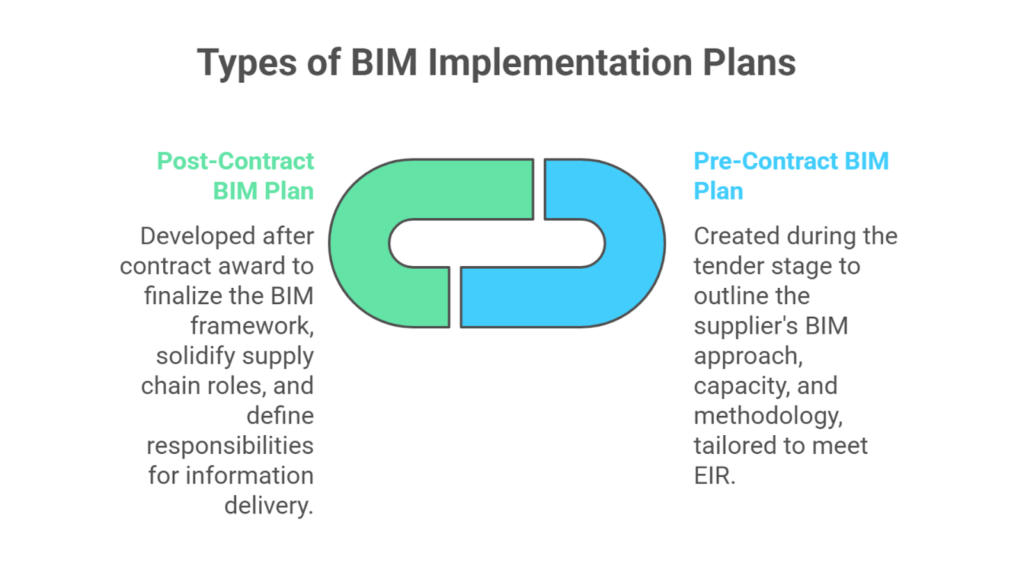
There are two main types of BIM Implementation Plans: the pre-contract BIM plan and the post-contract BIM plan. Each serves a specific purpose and contains information tailored to the project’s stage:
| Type of BIM Plan | Key Details |
| Pre-Contract BIM Plan | Created during the tender stage to outline the supplier’s BIM approach, capacity, and methodology. Tailored to meet Employer’s Information Requirements (EIR). |
| Post-Contract BIM Plan | Developed after contract award to finalise the BIM framework, solidify supply chain roles, and define responsibilities for information delivery. |
The pre-contract BIM plan sets the foundation by defining the initial approach. In contrast, the post-contract BIM plan builds upon that framework to finalise roles and responsibilities, ensuring seamless integration and delivery throughout the project lifecycle.
Together, these plans lay the groundwork for the steps of BIM implementation, ensuring a structured and practical approach to project execution.
4 Steps of BIM Implementation
Implementing Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a transformative process that improves efficiency, collaboration, and project outcomes throughout a project’s lifecycle. To fully realise its benefits, a structured approach is essential.
Breaking the implementation into clear and manageable steps enables organisations to seamlessly integrate BIM into their workflows, align their teams, and achieve their strategic goals.
The key steps of successful BIM implementation are as follows.
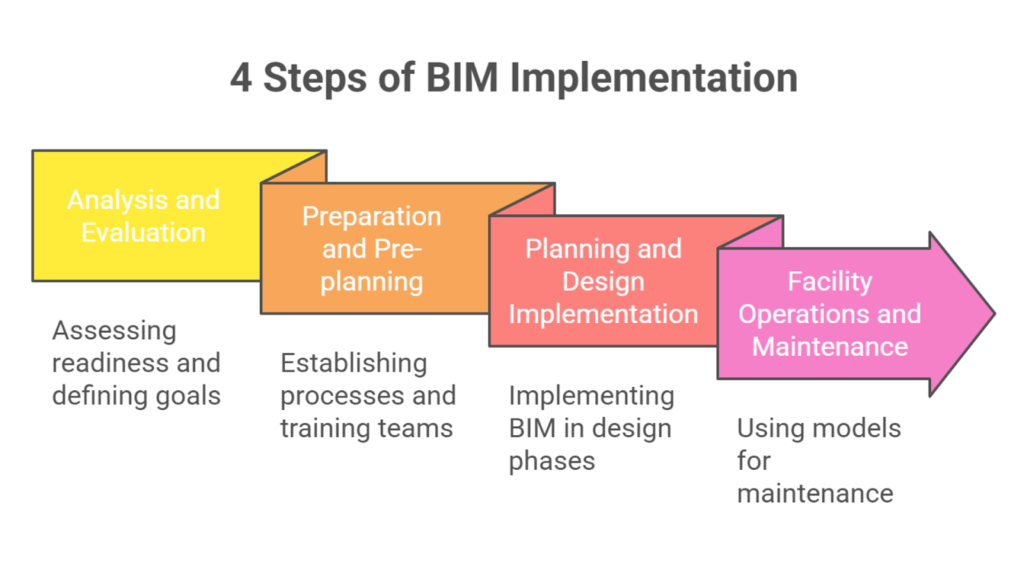
Step 1. Analysis and Evaluation
The initial step is to evaluate the organisation’s readiness for BIM adoption and assess the project’s specific needs. Publish the implementation plan and objectives for Building Information Modelling (BIM) within your organisation as part of an internal assessment process. The best practices that can help guide the initial phase of BIM implementation are:
- Assess Current Capabilities: Examine existing workflows, software, and team expertise to pinpoint BIM knowledge or technology gaps.
- Define Goals: Set clear objectives for implementing BIM, such as enhancing collaboration, improving visualisation, or optimising costs.
- Align Stakeholders: Identify key stakeholders and secure their support by emphasising how BIM benefits their roles. Conduct feedback sessions with the internal team to gather insights on adopting new technology, processes, and workflows.
- Evaluate Tools: Explore and select BIM tools and technologies that best match your objectives and project requirements.
Step 2. Preparation and Pre-planning
This step focuses on establishing the key elements necessary for seamless BIM integration. Standardising technology processes and ensuring teams are properly trained ensures the successful implementation of new technology. You can do pre-planning by:
- Develop a BIM Implementation Plan (BEP): Outline project-specific workflows, roles, and responsibilities to guide BIM implementation.
- Standardise Processes: Create clear guidelines for naming conventions, data exchange formats, and documentation standards.
- Establish Collaboration Protocols: Define how information will be shared and updated, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned.
- Train Teams: Conduct training sessions to address skill gaps and help teams become proficient with BIM tools and workflows.
Step 3. Planning and Design Implementation
This stage focuses on implementing BIM principles during the project planning and design phases. The execution of the plan should be a collaborative decision involving all stakeholders in the project. A BIM implementation plan includes the following components:
- Portfolio Management: Overseeing and coordinating multiple BIM projects within the organisation.
- Test Case-Based Planning and Implementation: Developing and testing specific scenarios to ensure the BIM system works as intended.
- Spatial Planning: Organising and optimising space utilisation throughout the project.
- Team Restructuring: Adjusting team roles and responsibilities to align with BIM processes and requirements.
- Information Handover: Ensuring accurate and comprehensive transfer of information between project phases and stakeholders.
- Defining New Roles and Responsibilities: Establishing clear roles for team members in the BIM process. This includes BIM managers, coordinators, and modellers who can execute the plan efficiently and effectively.
- Measuring Performance: Tracking and assessing the success of BIM implementation through key performance indicators (KPIs).
Step 4. Facility Operations and Maintenance
The high-level digital model created during the design phase can serve as a foundation for the operations and maintenance phase. The best practice is to use the building data from this model and modify it to include operations and maintenance details for the facility.
The key factors to consider when determining if the high-level design model can be effectively used for operations and maintenance are:
- Element Integration: Which elements were integrated into the model during the design phase, and how comprehensive is the model regarding building systems and components?
- Regular Updates: Was the digital model regularly updated to reflect the most current and accurate information, ensuring it stays relevant for the operations phase?
- Stakeholder Access: Were all authorised stakeholders able to quickly retrieve and utilise the data from the model, ensuring seamless collaboration and decision-making during operations and maintenance?
Every organisation has unique requirements and structures, so the activities carried out during the BIM stages may vary based on these needs. Establishing a clear, step-by-step process and following it carefully for a successful BIM adoption is crucial.
To maximise their potential, you can also use strategic approaches.
Also read: A Guide to Building Information Modelling (BIM) Impact on Modern Construction Industry.
7 Effective Strategies to Implement BIM in Your Construction Projects
Implementing Building Information Modelling (BIM) in construction projects can significantly enhance efficiency, collaboration, and project outcomes. Whether you’re new to BIM or looking to streamline your adoption process, the following effective strategies will guide you through a successful implementation.
1. Assemble a Skilled Team
Look for team members with experience in BIM software and processes. Also, include architects, engineers, contractors, and clients to encourage collaboration and a unified approach.
2. Invest in the Right Tools and Technology
Assess your current tools to ensure they can integrate with BIM processes. Check their cost estimation, scheduling, and clash detection capabilities to ensure they effectively support the BIM workflow. Popular tools like Revit, Navisworks, and BIM 360 help streamline processes.
3. Establish Standards and Protocols
Set standards for model creation, data sharing, and project documentation to maintain consistency and quality. BIM standards should include naming conventions for files and components, guidelines for modelling practices, and data management protocols to prevent conflicts and errors.
4. Focus on Collaboration
Implement a Common Data Environment (CDE) to centralise project information so all stakeholders can access, update, and share data in real-time. You can also use BIM to enhance teamwork by following these guidelines:
| Practices | Key Details |
| Regular Meetings | Schedule coordination meetings to review BIM models and address issues or challenges. |
| Collaborative Platforms | Use BIM collaboration tools to enable real-time updates and seamless communication among team members. |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Involve clients, contractors, and consultants in the BIM process to ensure alignment and informed decision-making. |
Implementing these practices fosters a collaborative environment, ensuring transparency, efficiency, and better decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
5. Monitor Progress and Adapt
Start with pilot projects or smaller teams to test BIM processes and identify areas for improvement. Track progress against your BIM goals and KPIs throughout the project. Actively seek feedback from team members and stakeholders and use it to refine workflows, tools, and processes, ensuring greater efficiency and better outcomes.
6. Integrate BIM into Facility Management
Integrating BIM into facility management enhances its value beyond construction by offering a comprehensive digital representation of the building. Facility managers can use these models to efficiently streamline repairs, monitor equipment lifecycles, and improve energy efficiency, ensuring smoother operations and better resource management.
7. Evaluate and Learn from the Project
At the end of the project, document the lessons learned to refine and enhance BIM processes for future projects. Focus on continuous learning to keep up with evolving technologies and industry practices. Ongoing improvement ensures that BIM implementation stays efficient and effective over time.
Ready to streamline your projects and achieve these benefits?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Revit Architectural and Structural Solutions. They coordinate with your team to develop, record, and streamline the BIM Revit Model, along with the sheets, Bill of Quantities, and Bill of Materials, and clash coordination.
Implementing BIM effectively requires a clear strategy and commitment to best practices. Continuous learning and improvement are essential for refining BIM processes and ensuring long-term success. Understanding the core features of BIM further highlights its transformative potential.
Key Features of BIM
Building Information Modelling (BIM) has transformed the construction industry by introducing advanced capabilities beyond traditional methods. Its multi-dimensional approach integrates various facets of a project, promoting collaboration, efficiency, and innovation.
Here are the key features of BIM:
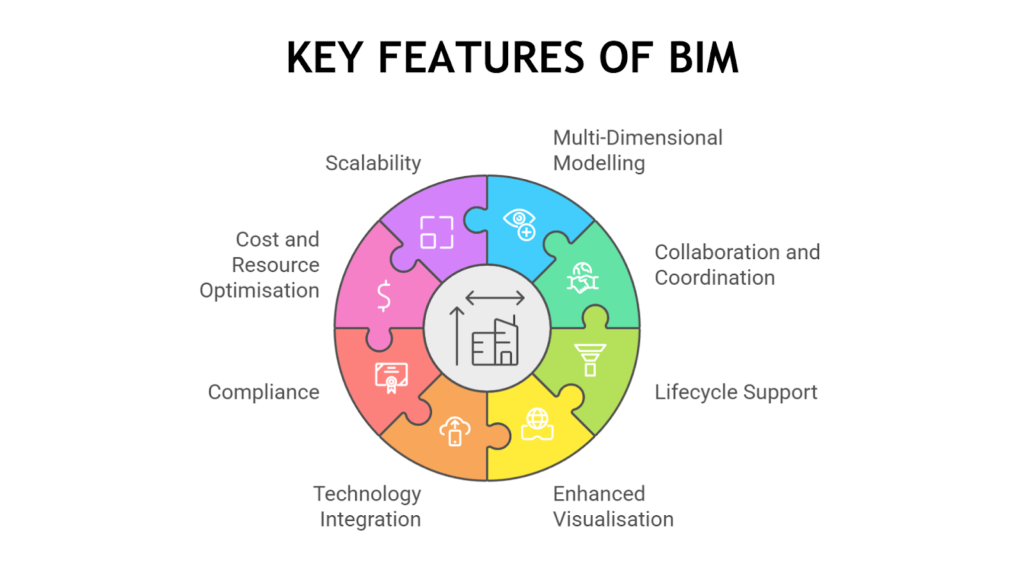
- Multi-Dimensional Modelling: Adds 4D (scheduling), 5D (cost), 6D (sustainability), and 7D (facility management) for lifecycle coverage.
- Collaboration and Coordination: Bridges communication gaps among stakeholders for seamless project execution.
- Lifecycle Support: Enhances design, construction, maintenance, renovations, and deconstruction processes.
- Enhanced Visualisation: Realistic 3D models, VR, and AR improve stakeholder understanding and engagement.
- Technology Integration: Incorporates GIS, IoT, and cloud platforms for smart management and remote collaboration.
- Compliance: Aligns with standards like ISO 19650 and certifications such as LEED and BREEAM.
- Cost and Resource Optimisation: Reduces waste, streamlines workflows, and identifies cost-saving opportunities.
- Scalability: Adapts to projects of all sizes, from small buildings to large infrastructure developments. BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.

Conclusion
Successful BIM implementation depends on a clear plan and effective teamwork. A well-structured roadmap aligns objectives, roles, and processes, while a skilled and collaborative team drives its successful execution.
Adaptability is equally critical throughout the BIM process. Embracing feedback, refining workflows, and adopting new technologies help teams enhance efficiency and achieve better outcomes. By blending strategic planning with adaptability, you can unlock BIM’s full potential and deliver efficient, cost-effective, and future-ready projects.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Architecture and Structure discipline. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: BIM Levels and Stages of Development Explained
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is BIM implementation?
A BIM implementation plan is a strategic guide that outlines how an organisation will adopt and use BIM in its projects. It helps integrate BIM workflows, tools, and practices effectively, ensuring the organisation meets its goals while improving efficiency.
2. What are the four phases of BIM implementation?
The four phases of BIM implementation are as follows:
- Analysis and evaluation
- Preparation and pre-planning
- Planning and design implementation
- Facility operations and maintenance
3. What is the main purpose of BIM?
BIM is used to create and manage data throughout a project’s design, construction, and operations phases. It combines data from multiple disciplines to produce detailed digital models managed on an open cloud platform for real-time collaboration.

