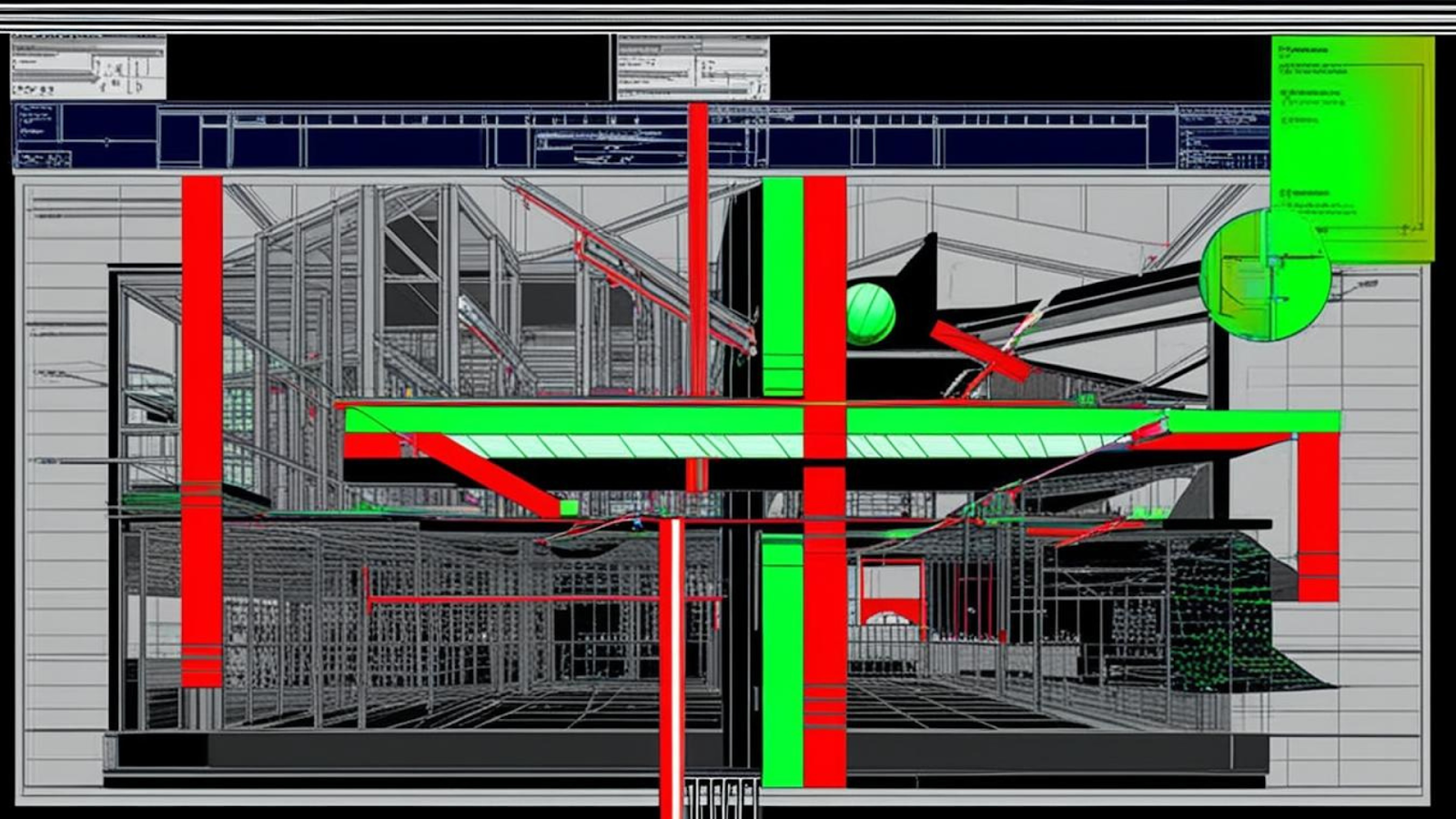
Research shows that 4-6% of total construction project costs are attributed to rework, and this only includes direct costs or reported instances. Unresolved clashes, such as design misalignments or workflow conflicts, are significant contributors to this rework, often resulting in costly delays and inefficiencies.
These challenges are common in construction projects and team collaborations, underscoring the need for proactive intervention. Taking a structured approach to finding and fixing conflicts has made clash detection an essential part of modern project management.
Effective clash detection is key to maintaining efficiency and harmony. It requires understanding the different types and causes of clashes and using advanced tools to resolve them.
This article covers the basics of clash detection, its benefits, how clashes are identified, actionable steps for resolution, and the latest software innovations that make the process smoother.
Understanding Clash Detection
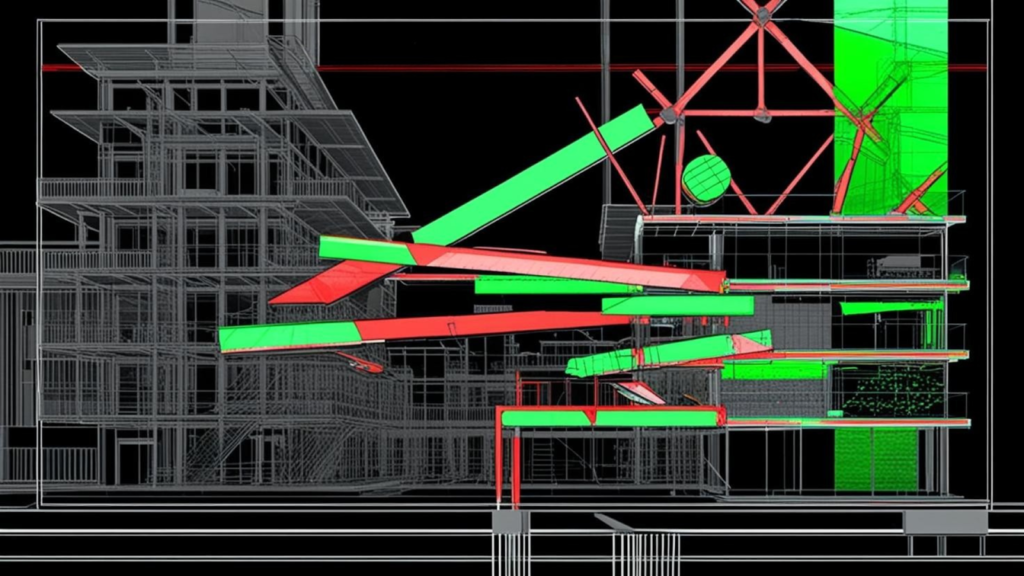
Clashes occur when different parts of a building’s design overlap or interfere in the same space. These conflicts often involve structural, architectural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEPF) systems. For instance, a duct might pass through a beam, or a plumbing pipe could block the path of electrical conduits.
Clash detection is the process of finding and resolving those conflicts between different systems or elements. These clashes happen when two or more components share the same physical space or fail to meet design requirements.
Addressing these issues early is essential, as it minimises costly rework, prevents delays, and enhances coordination across architectural, structural, mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEPF) systems.
However, it’s equally important to understand how clash detection differs from clash avoidance. Clash avoidance is a complementary strategy to prevent these issues from arising in the first place.
Differences Between Clash Detection and Clash Avoidance
Both clash detection and clash avoidance are essential for effective project management, but they serve different purposes. Clash detection focuses on identifying conflicts that have already occurred within a project, such as overlapping components or misaligned designs.
In contrast, clash avoidance takes a preventive approach by using strategies and planning techniques to minimise the chances of clashes happening in the first place.
The key differences between clash detection and clash avoidance are as follows:
| Aspects | Clash Detection | Clash Avoidance |
| Timing | Performed after the design is completed, during coordination and review. | Implemented during the design process to avoid potential conflicts. |
| Focus | Reactive: Identifies and resolves existing conflicts. | Proactive: Prevents conflicts from arising in the first place. |
| Tools Used | Clash detection software like Navisworks, BIM 360, or Solibri. | Collaborative design tools and adherence to standards, such as Revit and BIM guidelines. |
| Key Participants | Typically involves BIM coordinators and design teams during review phases. | Requires close collaboration among all design disciplines (architectural, structural, MEPF, etc.). |
| Effort Level | Focused on solving issues post-design, often requiring iterations. | Emphasises meticulous planning and collaboration to avoid rework. |
| Cost Implication | May involve additional costs if clashes require rework or design changes. | Reduces costs by eliminating the need for rework or delays during construction. |
| Outcome | Ensures a clash-free model before construction begins. | Produces a well-coordinated design from the outset. |
By combining clash avoidance with clash detection, you create a system that both prevents potential conflicts and responds to any that arise, ensuring smoother execution throughout every stage.
This approach not only minimises disruptions but also delivers significant advantages to projects. Knowing how clash detection contributes to successful project outcomes is crucial to understand its value.
Benefits of Clash Detection
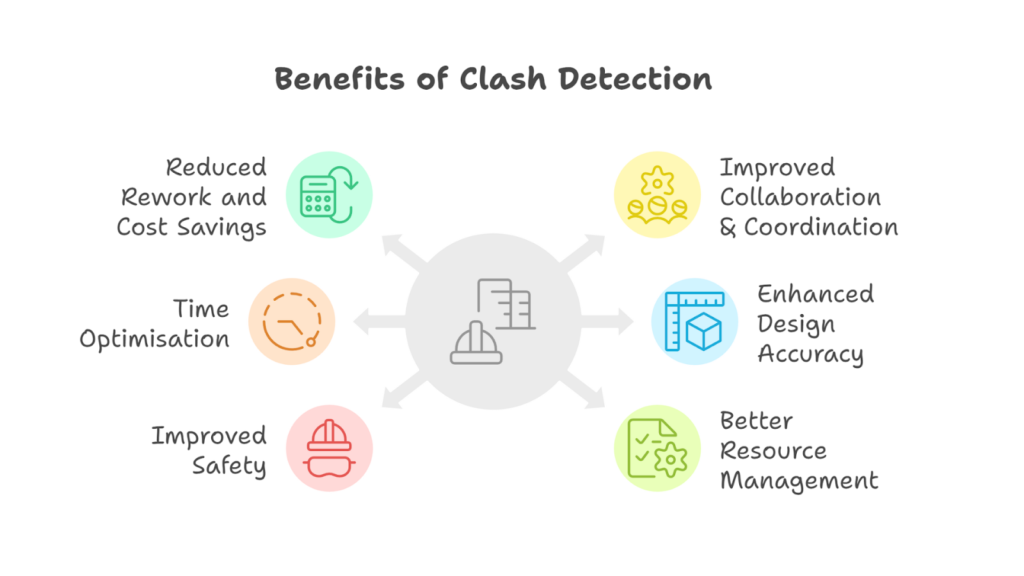
Clash detection is not just a problem-solving tool but an essential part of efficient project management. It improves communication, collaboration, and overall workflow in the construction industry.
Clash detection helps in a number of ways, such as:
- Identifying design conflicts early, reducing costly on-site changes, and preventing delays caused by unresolved clashes during construction.
- Improving communication among architects, engineers, and contractors. Aligning all stakeholders by bringing together various disciplines into a unified model.
- Speeding up the design and preconstruction stages by addressing conflicts before construction starts. Avoiding delays by resolving sequencing and workflow issues.
- Ensuring precise integration of architectural, structural, and MEP systems. Maintaining spatial and clearance requirements, leading to improved design outcomes.
- Reducing risks associated with physical clashes on-site, ensuring safer working conditions. Identifying potential hazards before they become real-world problems.
- Optimising material use by eliminating conflicting or unnecessary components and enhancing construction sequencing to make better use of labour and equipment.
- Showing a commitment to quality and efficiency with a clash-free model. Building trust by demonstrating proactive measures to avoid costly disruptions.
By leveraging clash detection tools, construction teams can identify and resolve conflicts early, paving the way for smoother project execution. Remember, clashes always vary in nature and complexity.
Also read: A Guide to Building Information Modelling (BIM) Impact on Modern Construction Industry.
Types of Clashes
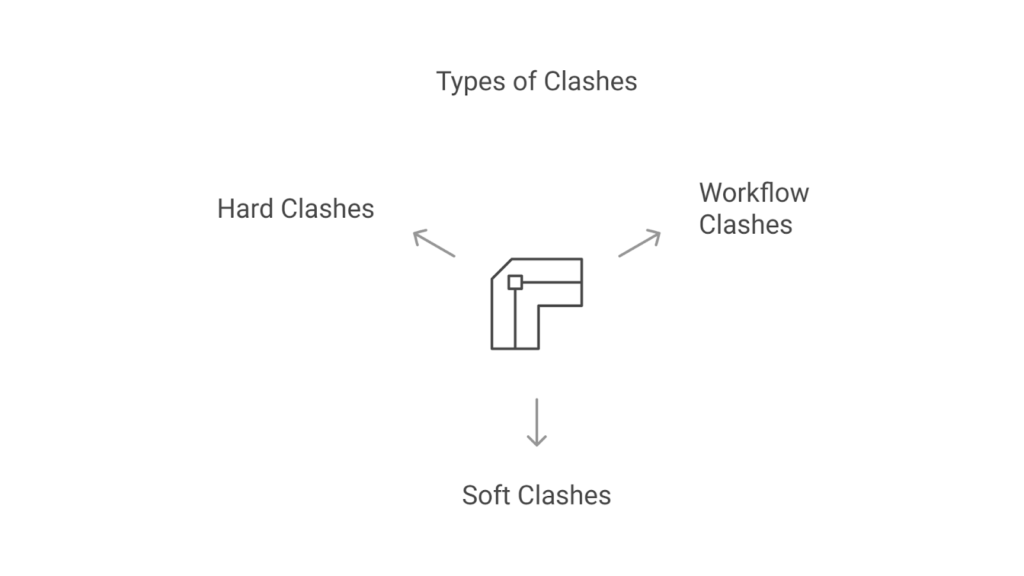
Clashes can happen at different project stages in the construction industry, often due to design errors, scheduling conflicts, or misaligned workflows. If not identified and resolved early, these clashes can disrupt progress, increase costs, and lead to rework.
The most common types of clashes in construction are as follows:
1. Hard Clashes
Hard clashes occur when two or more physical elements occupy the same space within a design or structure. These conflicts can stop construction activities and may require immediate redesign or rework, causing delays and increased costs.
Examples include a structural beam intersecting with a HVAC duct or electrical pipe/wiring/conduits conflicting with plumbing pipes.
2. Soft Clashes
Soft clashes involve components that don’t technically overlap but fail to meet spatial or design requirements, such as clearance or maintenance access. They can affect functionality or future maintenance, leading to inefficiencies and potential safety hazards.
Examples include a pipe installed too close to a wall, leaving insufficient room for maintenance, or HVAC systems positioned without proper airflow clearance.
3. Workflow Clashes
Workflow clashes occur when tasks, resources, or schedules overlap or conflict, causing delays or inefficiencies in the construction timeline. They can disrupt the construction schedule, leading to idle resources, labour conflicts, and cost overruns.
Examples include multiple teams scheduled to work in the same space at the same time or delays in material delivery due to uncoordinated timelines.
By identifying and addressing these clashes with the right tools and strategies, construction teams can make projects run more smoothly, avoid disruptions, and keep costs down.
Ready to streamline your projects and achieve these benefits?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Revit Architectural and Structural Solutions. They coordinate with your team to develop, record, and streamline the BIM Revit Model, along with the sheets, Bill of Quantities, and Bill of Materials, and clash coordination.
Causes of Clashes
Clashes in construction projects often occur due to a mix of planning, design, and execution issues. Identifying these root causes is essential for preventing conflicts, minimising delays, and reducing costs. Here are the primary causes of clashes in construction:
| Causes | Example |
| Inadequate collaboration between architectural, structural, and MEPF teams during the design phase. | A structural column designed without accounting for HVAC ducts. |
| Insufficient communication between stakeholders, including designers, contractors, and project managers. | Misaligned expectations about component placement due to unclear communication. |
| Using outdated or incomplete plans, models, or documentation during the design and construction. | An incomplete model that omits critical MEP components. |
| Increasingly sophisticated and dense building designs that leave little margin for error. | Tight spaces with overlapping systems, such as plumbing and electrical conduits. |
| Poorly planned timelines result in overlapping tasks or resource allocation issues. | Multiple teams are scheduled to work on the same floor simultaneously. |
| Mistakes during the design, planning, or execution phases due to oversight or miscalculation. | Incorrect dimensions entered into a 3D model. |
| Failure to leverage advanced clash detection tools or reliance on outdated manual processes. | Over-reliance on 2D drawings that fail to capture spatial conflicts. |
| Lack of standardised design protocols or construction practices across teams. | Different teams use incompatible file formats or modelling conventions. |
Understanding the causes of clashes is the first step in managing them effectively, but spotting these issues early is just as important.
How are Clashes Spotted?
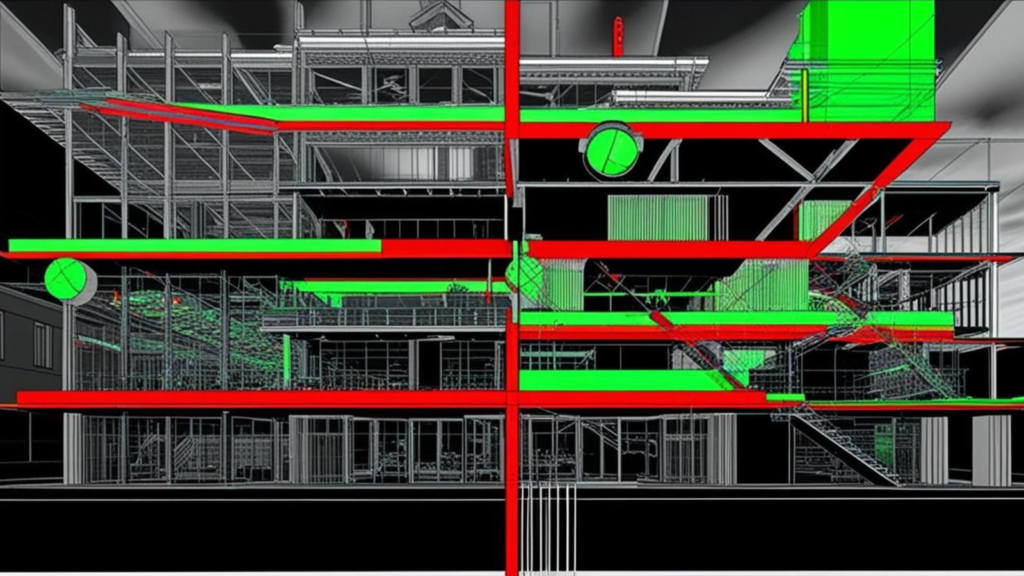
In the construction industry, identifying clashes early is key to avoiding costly delays, rework, and inefficiencies. Detecting clashes involves using technology, proactive planning, and teamwork across project teams. Here’s how clashes are typically detected in construction:
| Methods | Example |
| Tools like Navisworks and BIM 360 automatically detect overlaps and clearance issues. | Navisworks highlights a plumbing pipe clashing with a structural beam. |
| Multidisciplinary teams meet to review plans and discuss alignment. | An MEP team flags insufficient clearance for maintenance access. |
| Interactive 3D walkthroughs and simulations reveal hidden spatial issues. | A 3D walkthrough reveals a suspended ceiling interfering with sprinklers. |
| Software scans integrated models and generates clash reports for resolution. | A report identifies a column intersecting with an air duct. |
| Drones, sensors, and IoT devices capture data to compare with digital models. | A drone captures footage of a misaligned beam during construction. |
| AI analyses project inputs and historical data, alerting teams to deviations. | An AI tool alerts teams to a design that is failing clearance requirements. |
| Field teams document and communicate observed misalignments or conflicts. | A site worker reports a prefabricated wall not fitting due to a clash. |
| Platforms like Primavera P6 flag overlapping schedules or resource conflicts. | A scheduling tool flags two subcontractors assigned to the same area simultaneously. |
Identifying clashes effectively is just the first step in ensuring project success. Once identified, these conflicts must be addressed carefully to prevent disruptions and ensure smooth execution.
Steps to Resolve Clashes in Construction
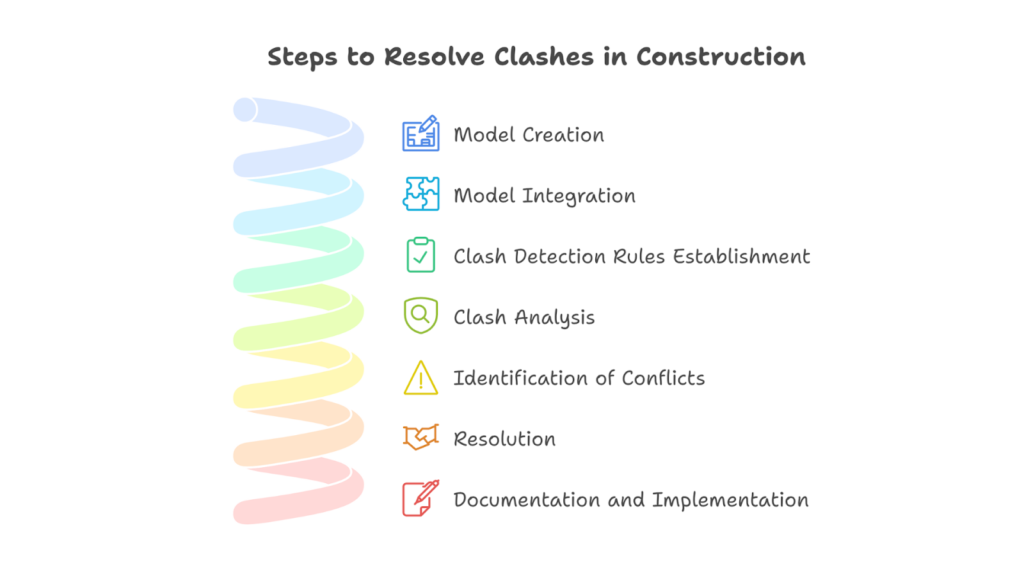
Whether it’s a design inconsistency, a scheduling conflict, or a resource overlap, resolving clashes requires a structured approach to address the root cause and implement actionable solutions. Understanding the steps to resolve clashes is crucial for maintaining timelines, controlling costs, and promoting team collaboration.
The steps to resolve clashes in construction are as follows:
- Model Creation: Create a detailed 3D model or BIM that represents the entire project, including architectural, structural, and system-specific components.
- Model Integration: Use BIM software to combine models from different disciplines into a single, coordinated model for clash detection.
- Clash Detection Rules Establishment: Set up clash detection rules based on project specifications and industry standards.
- Clash Analysis: Utilise specialised clash detection software to analyse the 3D models and identify any spatial conflicts or clashes between the integrated components according to the predefined rules.
- Identification of Conflicts: Review the clash detection reports for detailed information and prioritise addressing the conflicts that significantly impact the project’s success.
- Resolution: Work with the project team to resolve clashes by adjusting the design, modifying components, or coordinating the placement of conflicting elements.
- Documentation and Implementation: Document how clashes were resolved and update the 3D model, ensuring that all project participants are aligned and informed.
The clash detection process should be repeated after resolving conflicts to maintain quality. In addition, the 3D model should be continuously updated in response to design changes, with repeat clash detection as necessary to ensure coordination.
Conduct a final check before construction to ensure all potential issues have been treated and the model is accurate and ready for use. While ensuring the model is accurate and clash-free before construction is critical, technology can further enhance this process.
Advanced Software for Clash Detection
As construction projects become more complex, advanced software is essential for detecting and resolving clashes. These tools help make coordination easy, improve accuracy, and simplify collaboration. The advanced software for clash detection is as follows:
Integration of Revit with Other BIM Tools
Integrating Building Information Modelling (BIM) tools creates a unified environment for clash detection and resolution. This allows teams to identify & address issues across multiple models and disciplines effectively. Integration enhances clash detection by:
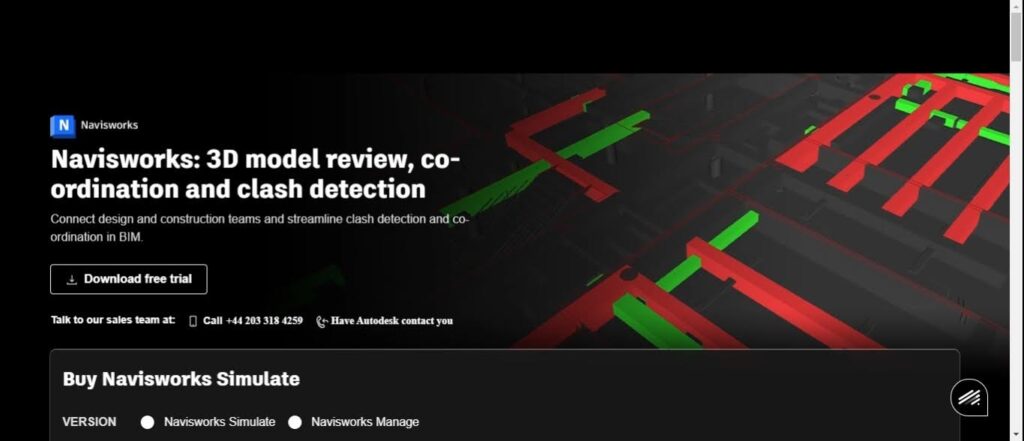
- Consolidating Data: Tools like Autodesk Navisworks integrate smoothly with other BIM software, creating a centralised platform where models from Revit, Tekla, and ArchiCAD can be combined for clash analysis.
- Interdisciplinary Coordination: Integration allows for cross-checking of architectural, structural, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) models for inconsistencies.
- Real-Time Updates: When tools are integrated, changes in one software (e.g., Revit) automatically update the clash detection software, ensuring the analysis stays current.
Autodesk Navisworks allows you to import models from Revit and other tools and perform detailed clash detection, ensuring that conflicts between structural elements and MEP systems are identified early.
In addition, BIM 360 offers a cloud-based platform for integrating multiple BIM tools. This enables teams in different locations to collaborate and effectively resolve clashes.
Use Revit’s Reporting and Visualisation Capabilities
Revit is a popular BIM tool used by 10.35% of industry professionals in the UK. It offers strong reporting and visualisation features supporting effective clash detection and resolution. Its detailed 3D visualisation helps stakeholders view clashes in context. In addition, clashes are highlighted with distinct colors, making them easy to spot quickly.
Revit enables users to isolate and inspect specific areas of a model, providing a more detailed analysis. It helps with:
- Customisable Clash Reports: Generate detailed reports documenting the location, type, and severity of clashes.
- Interactive Issue Tracking: Combine Revit with tools like BIM Track to track clashes and assign them to specific team members for resolution.
- Integration with Navisworks for Reporting: While Revit offers basic clash detection, exporting models to Navisworks enhances reporting and analysis with more advanced features.
Using AI and Automation Possibilities Within Revit
Artificial Intelligence (AI) & automation are transforming the clash detection process in Revit, making it faster and more efficient. AI algorithms predict potential clashes by analysing historical project data and current model inputs. It offers recommendations for resolving clashes based on best practices and past resolutions.
With AI improving predictive capabilities, automation in Revit further enhances this innovation by streamlining repetitive tasks and enabling real-time clash resolution. Automation helps in:
- Automated Clash Detection: Plugins like Dynamo and third-party integrations automate repetitive clash detection tasks, reducing human error.
- Real-Time Notifications: Automated workflows in Revit send immediate alerts when clashes occur, allowing for prompt action.
- Batch Processing: Automation tools can analyse multiple models or large projects simultaneously, saving significant time.
Autodesk Construction Cloud combines AI with Revit models to detect clashes, prioritise critical issues, and suggest solutions. In addition, the Clash Preventer tool monitors design activities in real time and warns users before a clash occurs. BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.

Conclusion
Clash detection plays a vital role in managing complex projects and collaborative workflows, helping to save time, reduce costs, and improve productivity. Organisations can minimise disruptions and ensure smoother operations by understanding the causes, types, and resolution steps of clashes.
Advanced tools and technologies, including AI and automation, make clash detection more accurate and efficient than ever. As technology evolves, clash detection will shift from reactive to proactive, changing how we manage projects and resolve conflicts.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for the Architecture and Structure discipline. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: BIM Levels and Stages of Development Explained.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Why is clash detection important?
Clash detection is vital in BIM coordination because it helps teams identify, analyse, and resolve issues before construction starts. Addressing conflicts at the design stage reduces rework, cuts material waste, and ensures the project stays on schedule and within budget.
2. Who is responsible for clash detection in BIM?
Typically, the BIM coordinator is responsible for clash detection and creating the clash detection matrix. This task is usually carried out during the project’s design phase.
3. Which software is best for clash detection?
Revit and Navisworks are two powerful software tools commonly used for clash detection.