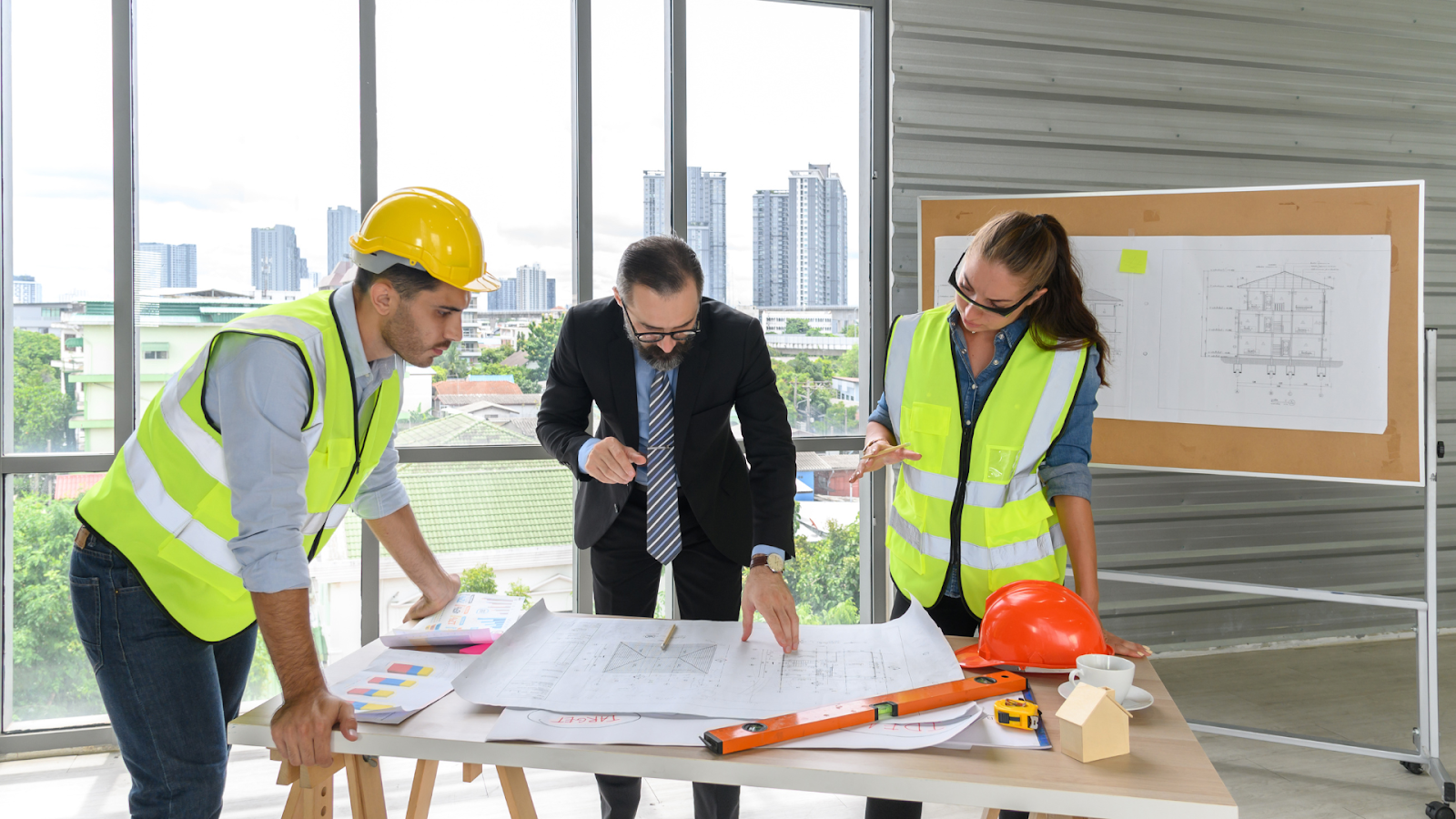
The global concrete market is expected to reach USD 821.6 billion by 2026, driven by the growing need for strong, long-lasting building materials. Concrete frame structures are popular because of their strength, flexibility, and durability.
Made of reinforced concrete beams, columns, and slabs, these frames create a solid structure that can support heavy loads and withstand forces like wind and earthquakes. Their reliability makes them ideal for residential, commercial, industrial, and infrastructure projects where long-term performance is essential.
To ensure stability, efficiency, and sustainability in modern construction, it’s essential to understand the concrete frame structures. In this article, you’ll learn about concrete frame structures, their different types, applications, concrete mix design, and much more.
Understanding Concrete Framework
Concrete framework, or formwork, is a mould that holds wet concrete in place until it hardens and gains strength. It plays a crucial role in concrete construction by ensuring the structure remains accurate, stable, and durable.
Formwork is very important in construction because it helps speed up the building process while keeping the quality high. It also reduces material waste and makes the construction eco-friendly. Additionally, it provides a stable working surface, which helps keep workers safe.
These benefits make formwork a crucial part of any construction project, ensuring quality and efficiency. Depending on the project’s requirements, different types of concrete framework are used to provide the necessary support and shape for the structure.
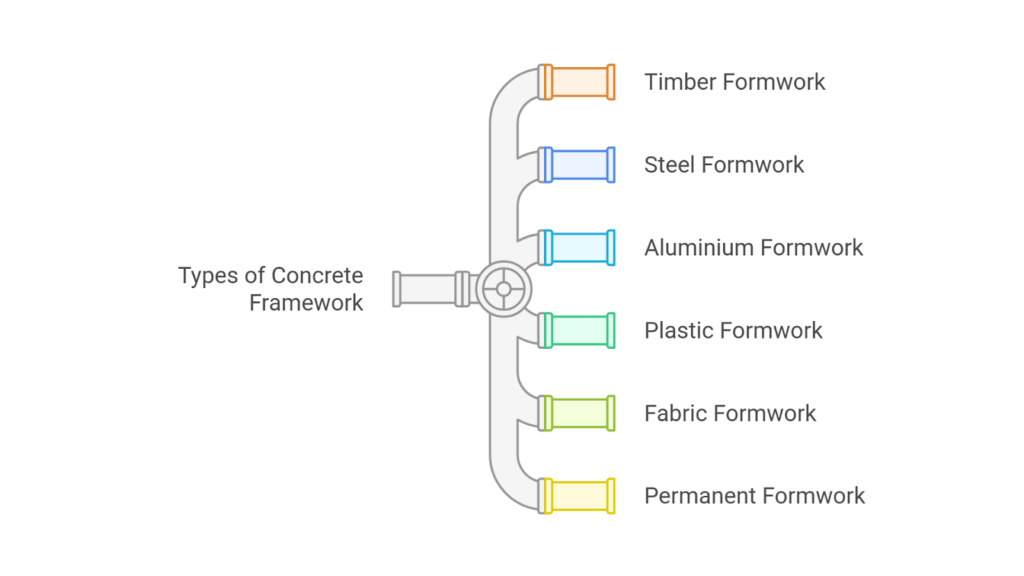
Types of Concrete Framework
Concrete framework consists of different types of formwork that offer varying levels of strength, flexibility, and ease of use. Understanding these types helps select the most efficient and cost-effective solution for different construction projects, ensuring precision, stability, and high-quality structural finishes.
Below is an overview of the types of concrete frameworks and their applications:
| Type | Key Details | Features | Applications |
| Timber Formwork | Made from wooden planks and plywood. | Lightweight, easy to construct, and ideal for small projects. Short lifespan compared to metal formwork. | Small-scale residential and commercial projects. |
| Steel Formwork | Composed of steel panels and frames. | High-strength, durable, reusable, and provides a smooth concrete finish. | High-rise buildings, bridges, and large-scale construction. |
| Aluminium Formwork | Lighter than steel but similarly durable. | Cost-effective, quick to assemble, and suitable for modular structures. | Mass housing projects, repetitive modular construction. |
| Plastic Formwork | Made from reinforced plastic panels. | Moisture-resistant, reusable, lightweight, and easy to install. | Small to medium-scale projects, wet environments. |
| Fabric Formwork | Uses flexible fabric sheets instead of rigid panels. | Allows for organic and curved shapes, reduces material usage, and enhances strength. | Unique architectural designs and complex geometries. |
| Permanent Formwork | Remains in place after concrete hardens. | Provides insulation, fire resistance, and additional structural support. | Precast concrete walls, fibre-reinforced structures, polystyrene block construction. |
Each type of concrete framework serves a specific purpose, but its effectiveness depends on certain key factors. A well-designed framework should provide stability, ensure precision, and contribute to the overall durability of the structure.
Qualities of Good Concrete Framework
A good concrete framework must be strong and rigid to support the weight of wet concrete without bending. It should be leak-proof to prevent the loss of cement slurry, which helps the concrete become stronger. Additionally, the formwork should provide a smooth finish for a high-quality surface with minimal defects.
Reusable metal and plastic formwork are cost-effective, helping to reduce project expenses. It should also be easy to assemble and remove, which makes the construction process more efficient, especially for large-scale projects.
Good formwork speeds up construction, but a building’s strength and durability come from its structural framework. Concrete frame structures create a strong and stable base, supporting different architectural and engineering needs.
What is a Concrete Frame Structure?
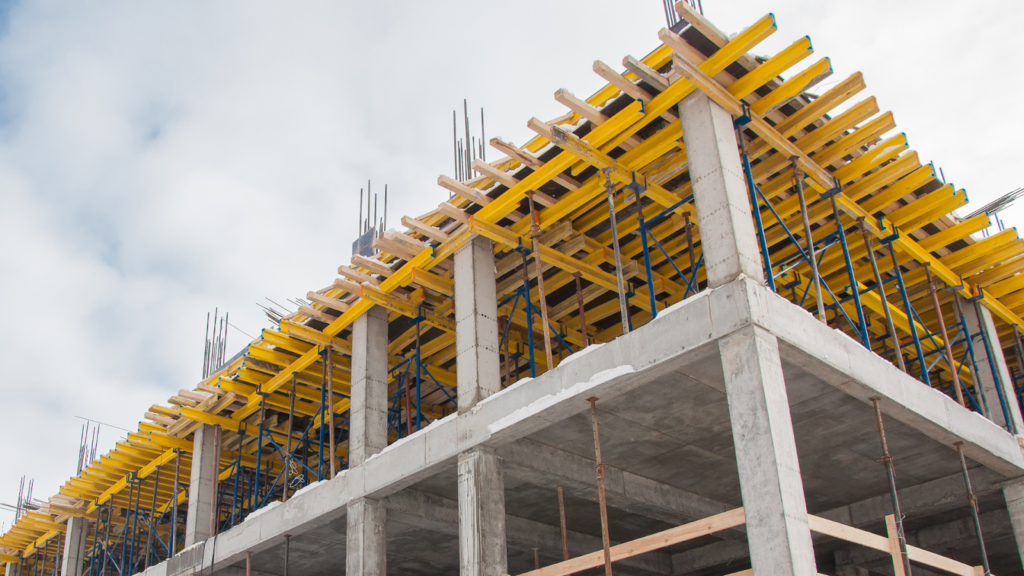

A concrete frame structure is a building made of strong concrete parts, such as beams, columns, and slabs. These parts hold up the building and distribute its weight evenly.
Columns are the main supports, carrying the load from the beams and slabs down to the foundation. Beams connect the columns and help support floors and roofs, while slabs create the actual spaces where people live or work.
Concrete frame structures are commonly used in homes, offices, and factories because they are strong, long-lasting, and resistant to fire and earthquakes. Their design is also very flexible, making them popular for tall buildings and multi-story constructions.
The benefits of concrete frame structures are as follows:
- High Strength and Load-Bearing Capacity: Can hold a lot of weight and stand up to forces like wind and earthquakes.
- Fire and Weather Resistance: Does not burn and can handle extreme weather, reducing damage.
- Design Flexibility: Can create large, open spaces, allowing unique and modern designs.
- Durability and Long Lifespan: Does not easily rust, rot, or wear out, keeping the structure strong for years.
- Better Sound and Vibration Insulation: Helps reduce noise between floors and rooms for a quieter space.
- Cost-Effective in the Long Run: Requires little maintenance and lasts long, saving money in the long run.
- Earthquake Resistance: Absorbs shock from earthquakes, making buildings more stable.
- Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance: Helps maintain indoor temperatures, lowering heating and cooling costs.
- Sustainable Construction Material: Can use recycled materials, reducing waste and environmental impact.
Understanding the benefits of concrete frame structures highlights why they are widely used in construction. However, steel frame structures also provide distinct benefits suited to different building requirements.
Key Differences between Concrete vs. Steel Frame Structure
Concrete and steel frame structures are two common types of construction systems, each with its own benefits.
Concrete frame structures use reinforced concrete beams, columns, and slabs, which make them very durable, fire-resistant, and effective at blocking sound. On the other hand, steel frame structures use steel columns and beams, which are more flexible, lighter, and allow for faster construction.
The key differences between concrete and steel frame structures are as follows:
| Factors | Concrete Frame Structure | Steel Frame Structure |
| Material Composition | Made of reinforced concrete (cement, sand, aggregate, and steel reinforcement). | Made of steel columns, beams, and joists. |
| Strength & Load-Bearing Capacity | High compressive strength, suitable for heavy loads. | High tensile strength, ideal for long spans and high-rise buildings. |
| Construction Time | Takes longer due to the curing time of concrete. | Faster assembly as steel components are prefabricated. |
| Weight | Heavy, requiring a strong foundation. | Lightweight, reducing foundation costs. |
| Durability & Maintenance | Highly durable and resistant to fire, moisture, and weather. Low maintenance. | Prone to corrosion and requires regular maintenance (coatings, painting). |
| Fire Resistance | Naturally fire-resistant, does not burn or lose strength at high temperatures. | Requires fireproof coatings or treatments to prevent structural failure in the fire. |
| Flexibility & Design Adaptability | Rigid structure with limited flexibility; best for multi-story and high-load buildings. | More flexible and adaptable to architectural changes, making it ideal for large-span structures. |
| Seismic Performance | Can absorb seismic forces when properly reinforced but is brittle under tension. | Excellent for earthquake-prone areas due to flexibility and ductility. |
| Sustainability & Environmental Impact | Uses natural resources; modern techniques incorporate recycled materials. | More eco-friendly as steel can be 100% recycled and reused. |
| Cost | Lower material costs but higher labour costs due to time-intensive construction. | Higher material costs but lower labour costs due to quick installation. |
| Lifespan | Long lifespan with minimal maintenance. | Long lifespan but requires periodic maintenance to prevent rust and degradation. |
The choice between concrete and steel frames depends on the project’s requirements, including durability, cost, and load-bearing capacity. Concrete frames are strong and flexible, making them useful for different types of buildings and industries.
Also read: Guide to Building Information Modelling (BIM) Impact on Construction Industry.
Where are Concrete Frame Structures Used?
Concrete frame structures are popular in construction because they are strong, long-lasting, and flexible in design. They can be used for different types of buildings, including homes, offices, and factories.
These frame structures can handle heavy loads, resist fire, and provide great insulation against heat and sound, making them a dependable option for modern buildings.
Some of the common uses of concrete frame structures are as follows:
1. Residential Buildings
Concrete frame structures are often used for apartments, condos, and tall residential buildings. They are strong and fire-resistant and help reduce noise, making homes safer and more comfortable. They also allow for multi-story buildings that make good use of space.
2. Commercial Buildings
Concrete frames are used in offices, malls, hotels, and mixed-use buildings because they are strong and flexible. They can support large open spaces, multiple floors, and heavy foot traffic while lasting long with little maintenance.
3. Industrial Facilities
Factories, warehouses, and manufacturing plants use concrete frames because they can hold heavy machines and loads. They are strong, fire-resistant, and can handle rough industrial work conditions.
4. Bridges and Infrastructure
Concrete frame structures are essential for bridges, flyovers, tunnels, and highways. They are strong enough to withstand heavy traffic, large loads, and harsh weather and last many years.
5. Educational and Institutional Buildings
Schools, universities, hospitals, and research centres use concrete frames because they are safe, strong, and need little maintenance. These buildings must support many people, medical equipment, and research activities.
6. Skyscrapers and High-Rise Buildings
Tall buildings and skyscrapers use strong concrete frames to stay stable and resist wind and earthquakes. This helps them grow taller while staying safe and energy-efficient. Reinforced concrete cores and shear walls further improve their structural integrity, ensuring long-term durability in extreme conditions.
7. Parking Structures and Transportation Hubs
Concrete frames are used in parking garages, airports, metro stations, and bus terminals to handle heavy traffic and large crowds. They are strong, fire-resistant, and long-lasting, making them important for city transportation.
8. Dams and Water Retaining Structures
Dams, reservoirs, and water treatment plants use concrete frames to hold back large amounts of water. They are built to handle strong water pressure and tough weather, ensuring they last longer.
Concrete frame structures are used for everything from big infrastructure projects to everyday buildings. Different types of concrete frames are chosen based on the project’s needs to ensure they are strong, efficient, and long-lasting.
Explore the best concrete solutions for your next project today.
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Revit Architectural and Structural Solutions. They coordinate with your team to develop, record, and streamline the BIM Revit Model, along with the sheets, Bill of Quantities, Bill of Materials, and clash coordination.
Types of Concrete Frame Structures
Concrete frame structures are grouped based on their design, how they carry weight, and how they behave under loads. Each type is used for different needs, depending on the building design, environment, and budget.
Choosing the right type of concrete frame helps balance safety and cost, ensuring the structure is strong and affordable. Below is an overview of the different types of concrete frame structures:
| Types | Key Details | Applications |
| Rigid Frame Structures | Beams and columns are rigidly connected to resist bending and shear forces, providing stability without additional bracing. | High-rise buildings, commercial complexes, and industrial structures. |
| Braced Frame Structures | Use diagonal braces made of concrete or steel to improve lateral stability, especially in seismic-prone areas. | Tall buildings, industrial structures, earthquake-resistant buildings. |
| Shear Wall Structures | Vertical reinforced concrete walls absorb lateral forces, preventing excessive horizontal movement. | Skyscrapers, hospitals, large residential buildings. |
| Flat Slab Structures | Slabs rest directly on columns without beams, creating open interiors and reducing construction time. | Office buildings, parking garages, shopping malls. |
| Waffle Slab Structures | Grid-like slabs with deep recesses improve load distribution while reducing material use. | Airports, auditoriums, commercial buildings. |
| Precast Concrete Frame Structures | Prefabricated beams, columns, and slabs are manufactured off-site and assembled on-site, ensuring faster and more precise construction. | Commercial buildings, bridges, modular construction. |
| Portal Frame Structures | Large-span rigid frames offer high load-bearing capacity with minimal internal obstructions. | Warehouses, factories, agricultural buildings. |
| Core Wall Structures | A central reinforced concrete core provides vertical and lateral stability, reducing external support needs. | High-rise towers, skyscrapers, elevator shafts. |
Each type of concrete frame structure is designed to meet specific building requirements, but strength and durability are key factors. Reinforced concrete frames take this further by incorporating steel reinforcement, improving their ability to withstand heavy loads & external forces.
What is a Reinforced Concrete Frame?
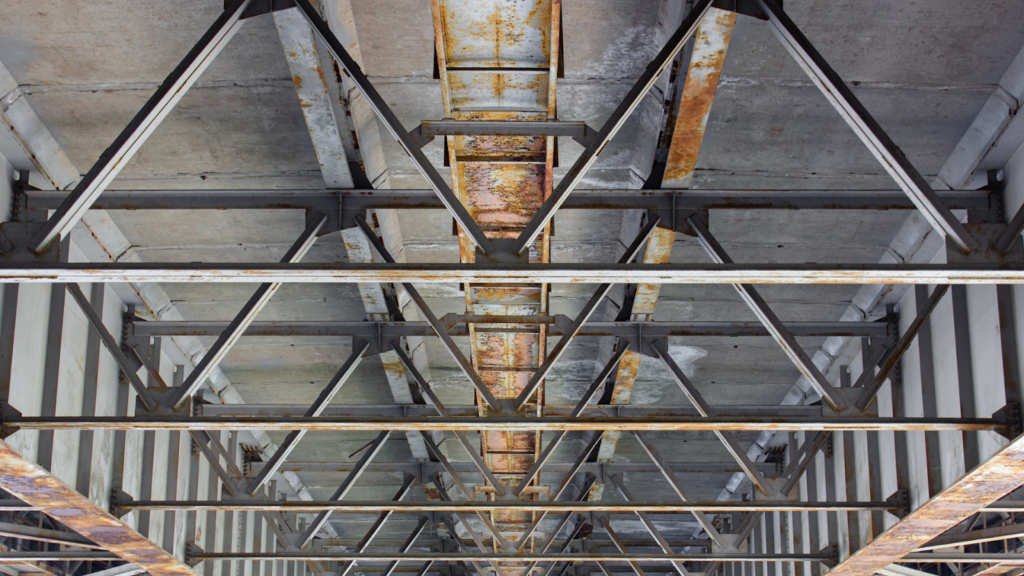

A reinforced concrete frame is a building structure made of concrete and steel bars for extra strength. This combination makes the building strong, long-lasting, and able to handle heavy loads, earthquakes, and strong winds. It is commonly used in homes, offices, and factories.
A reinforced concrete frame is very strong, durable, and can handle tough weather conditions, which makes it a popular choice in building today. By combining steel bars with properly set concrete, these frames provide long-lasting, stable support for different types of buildings.
Here’s a closer look at the process involved in creating a reinforced concrete frame:
1. Adding Steel Bars
Reinforced cement concrete is made by adding steel bars (called rebars) inside the concrete to strengthen it. While concrete is good at handling heavy weight, it isn’t as strong when pulled or stretched, so the rebars help give it extra strength.
2. Mould Holds Liquid Concrete
To shape the concrete, moulds or formwork hold the wet concrete in place until it hardens. These moulds are made to fit the exact shape needed for beams, columns, and slabs, ensuring the structure is built accurately.
3. Steel Rebars Are Tied Into a Reinforcement Cage
Before pouring concrete, steel rebars are tied together using steel wire to form a cage. This cage acts as the inner framework, adding extra strength to the structure and helping it resist bending, twisting, and stretching.
4. Mixing of Ingredients
Concrete is made by mixing cement, sand, stone chips (aggregates), and water. The right amounts of each ingredient ensure the mix is strong, durable, and easy to work with to build a solid structure.
5. Concrete Needs Curing
After pouring the concrete, curing is essential to help it become as strong as possible. Keep the concrete wet for a certain amount of time (usually 7 to 28 days) to stop it from drying out too quickly and cracking, ensuring the structure stays strong and lasts longer.
Curing helps concrete strengthen to handle heavy loads and harsh weather over time. Important structural parts also work together to stabilise and support the concrete frame.
Key Structural Components in Concrete Frame Structures
Concrete frame structures consist of various components that work together to provide strength, stability, and durability. Each element plays a crucial role in supporting loads and maintaining structural integrity.
The key structural components in concrete frame structures are as follows:
| Component | Key Details | Functions |
| Columns | Vertical load-bearing elements reinforced with steel. | Transfer structural weight to the foundation and resist compression and bending forces. |
| Beams | Horizontal structural members connecting columns. | Support loads from slabs and distribute weight to columns. |
| Slabs | Flat, horizontal elements forming floors and roofs. | Provide a working surface, distribute loads, and support structural integrity. |
| Foundations | The base of the structure anchored in the ground. | Transfer the building’s weight safely to the soil and provide stability. |
| Shear Walls | Reinforced concrete vertical walls placed strategically. | Resist lateral forces from wind and earthquakes, preventing excessive movement. |
| Core Walls | Reinforced concrete walls enclosing staircases and elevators. | Enhance the structural stability of high-rise buildings against seismic and wind forces. |
| Bracings | Diagonal reinforcements used in conjunction with beams and columns. | Provide extra lateral support, especially in earthquake-prone areas. |
| Lintels | Small horizontal beams placed above door and window openings. | Support the load above openings and prevent structural cracks. |
A concrete frame structure stays strong and stable, but the quality of the concrete is just as important. A well-planned concrete mix design ensures the right balance of strength, durability, and workability for different construction needs.
Concrete Mix Design
Concrete mix design is the process of choosing the right amounts of cement, sand, stone, and water to make concrete that is strong, durable, and easy to work with. A good mix design ensures the concrete performs well and reduces waste and cost.
The mix design process involves choosing the right amounts of cement, sand, stone, and water based on the project’s needs. The proportions affect the strength, ease of use, and durability of the concrete, as well as its ability to handle changes in moisture and temperature.
Things like the amount of water, the size of the stones, and any added chemicals also help improve the mix. By carefully adjusting these elements, the concrete mix can achieve the desired strength and durability for various applications.
Standard mixes are classified based on their compressive strength, providing a clear guideline for selecting the right mix for different structural needs.
Standard Mixes Indicate Compressive Strength
Concrete mixes are classified by their strength, measured in megapascals (MPa), after 28 days of curing. Concrete curing is a crucial process that ensures the material gains its intended strength and durability. It involves maintaining adequate moisture, temperature, and time to prevent cracking and enhance structural integrity.
The classification system ensures that the right mix is used for different structural applications, from residential buildings to high-load infrastructure projects.
Some common mix grades are:
- M20 (20 MPa): Used for residential buildings and pavements.
- M30 (30 MPa): Used for reinforced concrete structures that need extra strength.
- M40 (40 MPa): Ideal for strong infrastructure like bridges and tall buildings.
Higher grades mean the concrete is stronger and more durable, making it better for structures that carry heavy loads or face tough conditions.
Stronger concrete ensures a solid foundation, but the materials used for walls and cladding also play a crucial role in the structure’s durability and performance.
Walls and Cladding Materials in Concrete Frame Structure
The walls and outer coverings of concrete frame structures are crucial for providing protection, insulation, and stability and for contributing to the overall appearance of the building. Depending on the specific requirements of the building, these materials can vary in weight, strength, and durability.
Some common walling and cladding options used in such structures are as follows:
Walling Options: Heavier Walls
Masonry walls made from bricks, concrete blocks, or stone are durable, provide good insulation, and help reduce noise. They are used to strengthen buildings and support or carry weight.
Heavier walls add more weight to the building, so stronger foundations and extra support are needed.
Walling Options: Lighter Walls
Drywall partitions with steel or wooden frames are often used for internal walls in modern buildings. These walls are quick to install, flexible, and easy to change, and they are also lighter, reducing the load on the structure.
Lightweight walls are perfect for offices, commercial spaces, and homes where flexibility is important.
Cladding Options
Cladding materials protect, insulate, and improve the look of concrete frame structures. Some common cladding materials include:
- Glass: Often used in tall buildings to let in natural light and improve energy efficiency.
- Aluminium Panels: Lightweight, strong, and rust-resistant, used on modern building exteriors.
- Stone Sheets: Materials like granite, marble, and sandstone add beauty and strength to the outside of buildings.
- Ceramic Facades: Help protect buildings from weather and keep them insulated, often seen in modern designs.
Load-Bearing Capability for Cladding
Concrete frame structures support heavy cladding materials, like brick walls, to keep the building strong and stable. Load-bearing walls carry weight directly to the foundation, while non-load-bearing walls just enclose the space without supporting weight.
Lighter materials, like glass and aluminium panels, need special systems to hold them securely to the concrete frame. BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.

Conclusion
Concrete frame structures are an important part of modern construction because they are strong, flexible, and long-lasting. They create a solid base for all kinds of buildings, from houses to tall skyscrapers.
They are also fire-resistant, need little maintenance, and can be used in many types of projects. As urbanisation grows, concrete frame structures will play a key role in building safe, durable, and future-ready buildings.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for the Architecture and Structure discipline. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: BIM Levels and Stages of Development Explained.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is a concrete framework?
Concrete formwork is a mould or frame that holds wet concrete in place until it hardens and takes the shape needed for construction. It can be temporary, removed after the concrete sets, or permanent.
2. What is the frame for concrete called?
A concrete frame, also called a concrete skeleton, consists of beams, columns, and slabs that support a building or structure.
3. Is concrete frame a construction?
Yes, a concrete frame is a common type of structure made from columns and beams that form the main support system, or “skeleton,” of a building.

