The construction industry is changing, and technology is improving both efficiency and collaboration among teams. One significant advancement is 4D BIM (Building Information Modelling), which adds a time dimension to 3D models.
By adding this time factor, 4D BIM helps teams see project schedules, track progress in real time, and link construction tasks to a digital model. This makes it easier to spot scheduling problems early, manage resources better, and keep projects on track.
In this article, you’ll learn about BIM dimensions, key components of 4D BIM, and real-world applications in construction. In addition, you’ll explore the challenges of using 4D BIM, the role of the 4DCG EIR Template in managing information, and how 4D planning is shaping the future of construction.
What are BIM Dimensions?

BIM dimensions refer to different types of information added to a building project to improve planning, construction, and management. These dimensions help architects, engineers, and builders work more efficiently by providing detailed insights beyond just a 3D model.
Each dimension adds a new layer of data, making projects easier to design, build, and maintain. The most common BIM dimensions include:
2D BIM
This is the most basic form of BIM and consists of traditional blueprints and drawings. It provides a flat, two-dimensional representation of a building’s design, primarily used for initial planning and construction documentation. While limited in scope, it serves as a foundation before integrating more advanced BIM dimensions.
3D BIM
This is the most widely used dimension that showcases the physical structure and spatial characteristics of a building. It includes detailed geometry and design elements such as walls, roofs, and structural components, enabling teams to visualise the project in three dimensions. This improves coordination and helps detect clashes early in the design phase.
4D BIM
By incorporating the element of time, 4D BIM links the construction schedule with the 3D model. This allows project managers to simulate the construction process, visualise project progression, and ensure tasks follow the correct sequence. The result is improved planning and reduced risk of delays.
5D BIM
5D BIM integrates cost data with the 3D and 4D models. Connecting design, scheduling, and budgeting enables real-time cost estimation and financial forecasting. This ensures projects stay within budget while allowing teams to assess the financial impact of design changes.
6D BIM
Focused on sustainability, 6D BIM incorporates environmental data to evaluate a building’s long-term performance. It includes energy efficiency, carbon footprint, and resource usage, helping teams make informed decisions on materials and systems that improve sustainability.
7D BIM
7D BIM extends into facility management by providing essential data for building maintenance. It includes information on equipment, maintenance schedules, warranties, and operation manuals, ensuring efficient building management throughout its lifecycle.
8D BIM
This is the latest addition to BIM dimensions that emphasises safety management. It integrates safety planning into design and construction by identifying potential hazards and establishing safety protocols. Simulating different scenarios and providing safety-related data helps improve worker safety and reduce job site risks.
Each BIM dimension plays a role in making construction projects more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable. One of the key BIM dimensions that improves project planning and execution is 4D BIM.
Understanding 4D BIM in Detail
4D BIM (Time Dimension) integrates the 3D model with the project timeline, providing a clear visual representation of how construction will unfold over time. Connecting building components with scheduling and sequencing enables teams to simulate the construction process and improves planning and coordination.
This approach helps optimise resource allocation, simplify workflows, and ensure tasks are completed in the right order. Additionally, 4D BIM allows teams to track project progress, anticipate potential delays, and resolve conflicts before they impact the schedule. This improves efficiency, reduces risks, and supports better decision-making throughout the project.
By integrating scheduling data with 3D models, 4D BIM changes how construction projects are planned and executed.
Also read: A Guide to Building Information Modelling (BIM) Impact on Modern Construction Industry.
Use Cases of 4D BIM in Construction Projects
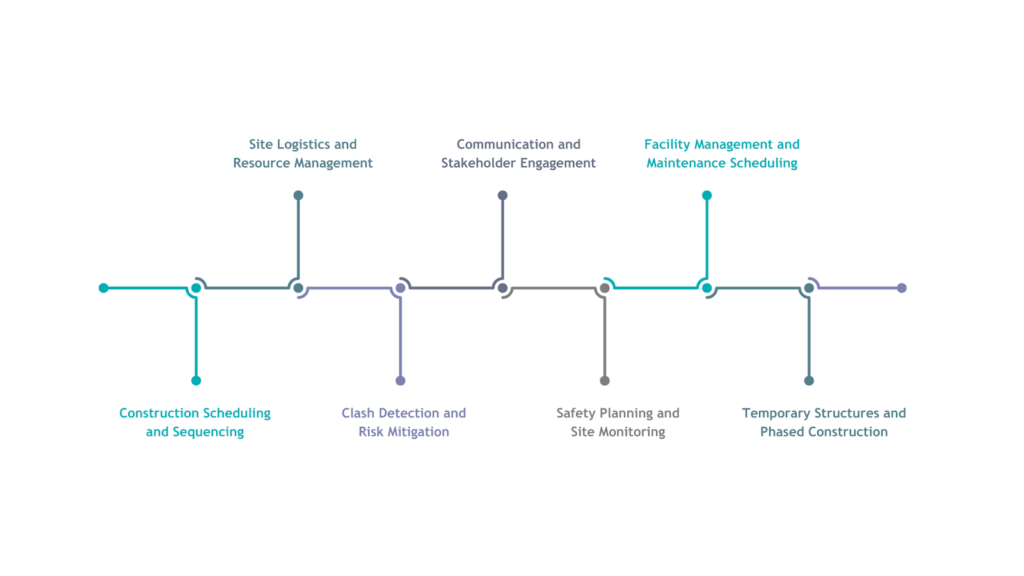
4D BIM allows teams to see and plan each stage of the project more effectively. It is used in many real-world applications, from organising construction sequences to improving site logistics and safety planning.
By simulating the entire building process, 4D BIM helps teams spot potential issues early, improve coordination, and keep projects on track. Some common use cases of 4D BIM in construction projects are as follows:
- Construction Scheduling and Sequencing
4D BIM helps project managers link the construction schedule to the 3D model, creating a clear visual of how different phases will unfold over time. For example, large projects like bridges or highways can show the excavation sequence, foundation work, structural framing, and finishing.
- Site Logistics and Resource Management
Managing materials, equipment, and labour on complex projects can be challenging. 4D BIM helps visualise when and where materials should be delivered, how machinery will be used, and how labour is allocated.
For instance, in high-rise construction, it can track crane movements and heavy equipment usage over time, preventing clashes and improving efficiency.
- Clash Detection and Risk Mitigation
By integrating the project schedule with the 3D model, 4D BIM helps detect conflicts in timing or resource allocation. If two tasks are planned for the same space at the same time, it can flag the issue in advance.
For example, hospital construction can highlight scheduling conflicts between mechanical and electrical installations, allowing adjustments before delays occur.
- Communication and Stakeholder Engagement
4D BIM improves communication by providing a clear, visual timeline of the construction process. This helps all stakeholders—including investors, architects, engineers, and contractors—understand project progress and make informed decisions.
For example, in public building projects, 4D BIM can be used in meetings to show updates, explain the impact of changes, and gather feedback.
- Safety Planning and Site Monitoring
Safety is a top priority in construction, and 4D BIM helps by identifying potential hazards before work begins. In large commercial developments, it can visualise high-risk tasks like crane operations or work at heights, ensuring proper safety measures are in place.
Project managers can use it to schedule inspections, monitor hazardous activities, and enforce safety protocols to reduce accidents.
- Facility Management and Maintenance Scheduling
4D BIM is also useful beyond construction, helping manage a building’s long-term maintenance. By linking the model to maintenance schedules, building owners can plan inspections, repairs, and upgrades efficiently.
For example, 4D BIM can schedule HVAC servicing, painting, and elevator maintenance in office buildings, keeping the facility in top condition over time.
- Temporary Structures and Phased Construction
For projects that require temporary structures—such as scaffolding, site offices, or access roads—4D BIM can model their setup and removal. For instance, stadium construction can show when to install temporary seating, worker facilities, and barriers, ensuring they are in place when needed and removed without disrupting progress.
Effective use of 4D BIM relies on several key components that bring together scheduling, visualisation, and data management. By integrating these elements, project teams can better coordinate tasks, anticipate challenges, and maintain smooth workflows.
Ready to simplify your projects and achieve these benefits?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Revit Architectural and Structural Solutions. They coordinate with your team to develop, record, and streamline the BIM Revit Model, along with the sheets, Bill of Quantities, Bill of Materials, and clash coordination.
Components of 4D BIM
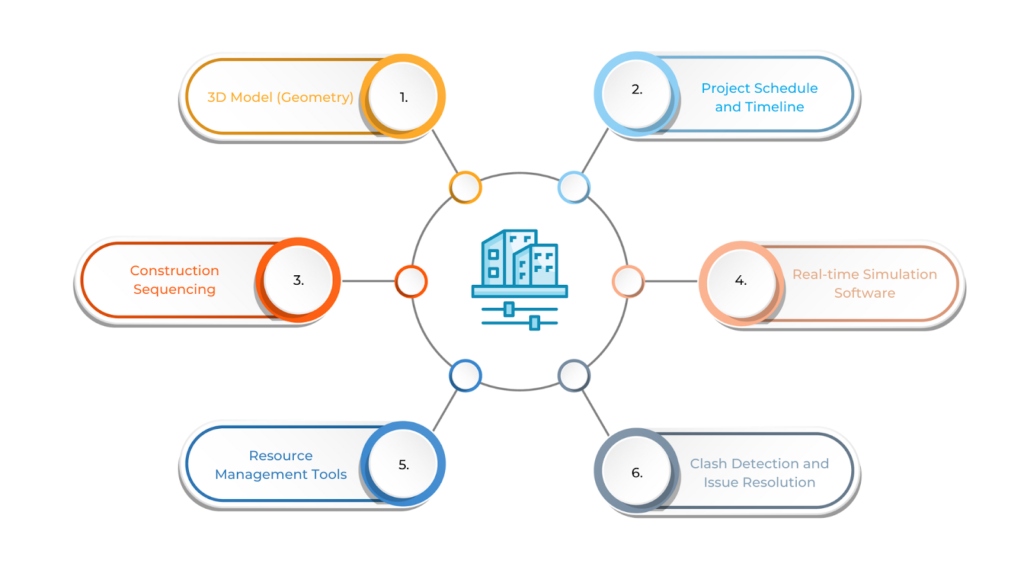
To make the most of 4D BIM, several essential components work together to manage the entire construction process effectively. These include a detailed 3D model of the building, project scheduling data, tools for sequencing construction activities, and real-time simulation software.
Additionally, these components must be integrated smoothly to ensure accurate, up-to-date information is accessible to all stakeholders involved in the project. The core components of 4D BIM include:
- 3D Model (Geometry)
The foundation of 4D BIM is a detailed 3D model that represents the physical structure of the building or infrastructure. This model includes key elements such as walls, floors, roofs, HVAC systems, plumbing, and structural components. It serves as the visual and spatial reference for the entire project, allowing teams to see how construction will progress over time.
- Project Schedule and Timeline
A critical part of 4D BIM is the construction schedule, which outlines the timeline for each phase of the project. This schedule details the start and end dates of tasks, from site preparation to final construction.
Typically managed through project management software like Primavera P6 or Microsoft Project, this data helps create accurate time-based simulations.
- Construction Sequencing
This component focuses on the logical order of construction activities, showing how different tasks depend on one another. By linking these activities to the 3D model, teams can visualise the sequence of work and optimise the flow of tasks. This helps ensure a smooth construction process and prevents scheduling conflicts.
- Real-time Simulation Software
4D BIM software visualises the 3D model according to the project schedule, allowing teams to simulate the construction process. This provides real-time visual feedback, helping project managers track progress, anticipate potential delays, and adjust the sequence of activities when needed.
- Resource Management Tools
To ensure efficient use of materials, labor, and equipment, 4D BIM integrates resource management tools. These tools help teams plan when and where specific resources are needed, preventing shortages and improving coordination. For example, teams can schedule the use of cranes or scaffolding at the right time to avoid bottlenecks.
- Clash Detection and Issue Resolution
4D BIM combines the 3D model and project timeline to identify scheduling conflicts and spatial clashes before construction begins. This allows teams to resolve potential issues early, reducing costly delays and rework.
By integrating these components, 4D BIM creates a more efficient, collaborative, and risk-free construction process, ensuring projects stay on track and within budget. While 4D BIM offers significant advantages, its implementation comes with some challenges.
Overcoming Challenges While Using 4D BIM
Integrating time with 3D models, managing project schedules, and allocating resources properly can be tough, especially in large or fast-moving projects. On top of that, coordinating with many stakeholders, keeping data up to date, and ensuring the software works well together can add to the complexity.
Addressing these challenges is key to unfolding the full potential of 4D BIM in construction. Below are the challenges while using 4D BIM and their effective solutions:
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Complex integration of time and space | Use advanced scheduling tools and BIM software, such as Navisworks, with strong integration capabilities.Divide the project into smaller, easier-to-manage phases and use well-defined task dependencies. |
| Data management and accuracy | Regular data validation, real-time updates, and central data management platforms to ensure accurate and up-to-date information. |
| Software and system compatibility | Choose BIM software like Autodesk Revit that supports integration with other tools.Use cloud-based platforms or middleware solutions for better compatibility across systems. |
| Collaboration and communication across teams | Implement structured collaboration plans, cloud-based project management tools, and regularly scheduled meetings to ensure smooth communication. |
| Training and expertise | Invest in training programmes for all team members and consult experienced BIM professionals to help with implementation. |
| High initial setup cost | Start with pilot projects to test the software’s effectiveness and gradually scale up as benefits are realised.Emphasise long-term savings and efficiency improvements. |
| Resistance to change | Clearly communicate the advantages of 4D BIM and provide case studies of successful implementations.Involve key stakeholders early in the process to reduce resistance. |
By addressing these hurdles head-on, construction teams can fully use the power of 4D BIM to improve project efficiency, reduce risks, and deliver high-quality projects on time and within budget.
To support the effective implementation of 4D BIM, structured tools are needed for proper information management and coordination. One such tool is the 4DCG EIR Template, which helps define and manage project requirements.
What is The 4DCG EIR Template?
The 4DCG EIR Template is a structured tool that supports 4D BIM by defining the Employer’s Information Requirements (EIR) as part of the 4D Construction Gateway (4DCG) initiative. It improves project efficiency by specifying the necessary information at various stages of construction.
The template specifies the data that contractors and project teams must provide, such as construction schedules, resource management details, and task sequencing. By integrating this information into the BIM model, teams can track progress, manage resources, and identify potential risks early.
The 4DCG EIR Template promotes standardisation and enhances stakeholder collaboration by setting clear expectations for data capture, delivery, and communication, leading to smoother project execution and successful outcomes.
As more of the construction industry adopts digital solutions, the role of 4D BIM is expected to grow even further.
Future Development and Industry Adoption of 4D BIM
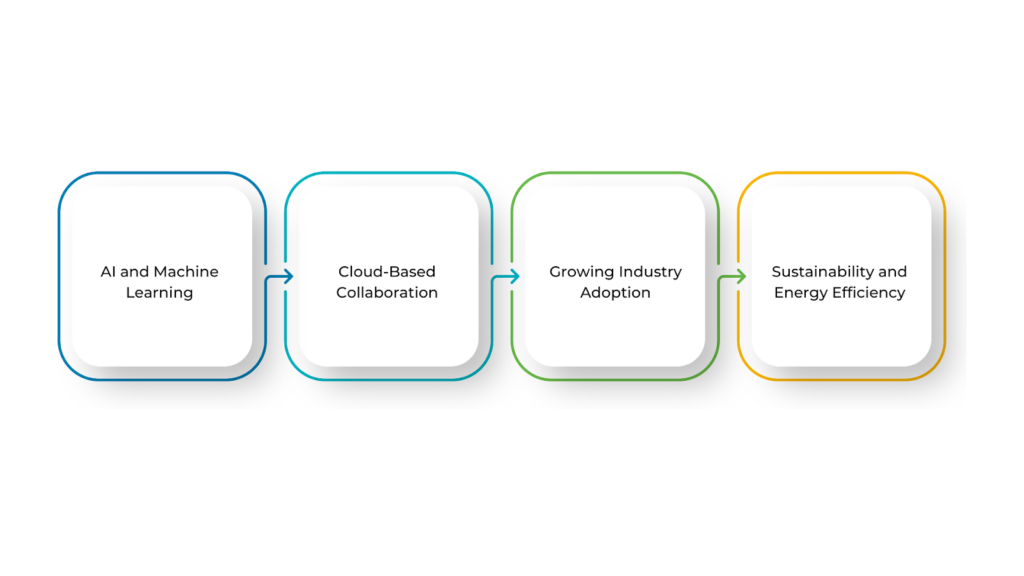
The future of 4D BIM looks promising as the construction industry moves further into digital technology. With ongoing advancements, 4D BIM will become more connected and efficient, offering new tools to handle complex projects.
Improvements in data sharing, automation, and real-time collaboration will help teams make better decisions and manage projects more effectively. Below are the future predictions regarding 4D BIM:
- AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are making 4D BIM smarter by automating tasks like scheduling, detecting risks, and optimising workflows. These technologies analyse large amounts of project data, spot patterns, and predict delays.
This helps teams make quick, informed decisions and adjust their plans in real-time. With AI, 4D BIM improves accuracy and efficiency, simplifying the management of complex construction projects.
- Cloud-Based Collaboration
Moving 4D BIM to the cloud allows project teams to work together more efficiently. Cloud-based platforms give stakeholders real-time access to project data, making it easier to track progress and make updates from anywhere.
This improves decision-making and helps teams respond quickly to changes, reducing delays. Cloud integration also connects 4D BIM with project management and budgeting tools, creating a smoother workflow.
- Growing Industry Adoption
More construction companies are using 4D BIM, especially in large infrastructure and commercial projects. As the benefits of improved scheduling, resource management, and risk reduction become increasingly evident, even smaller firms are beginning to adopt it.
With BIM software becoming more affordable and training more accessible, businesses of all sizes can utilise its capabilities.
- Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
4D BIM is playing a key role in sustainable construction by helping reduce waste and improve energy efficiency. It allows teams to simulate the construction process and evaluate environmental impacts, such as material usage and energy consumption.
By integrating green building strategies, 4D BIM supports sustainability goals and ensures projects meet environmental standards. As the construction industry embraces digital transformation, the role of 4D BIM in project planning continues to expand.
Is 4D Planning and BIM the Future for Project Success?
4D planning combines a 3D construction model with the project schedule, adding the element of time. This allows teams to visualise project progress, understand the sequence of activities, and identify potential scheduling conflicts before construction begins. By improving planning, communication, and collaboration, 4D planning helps ensure smoother execution.
As construction projects become more complex, 4D planning is emerging as a key tool for success. It links schedules to 3D models, providing clear insights into each phase and showing potential issues early. Studies show that organisations using 4D planning achieve three times better project outcomes than those without.
It improves coordination, prevents delays, and enhances stakeholder communication, reducing misunderstandings and keeping projects on track. More than just a trend, 4D planning and BIM are changing the industry, increasing efficiency, and ensuring project success.
BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.
Conclusion
4D BIM can change the construction industry by making project planning and execution more efficient, visual, and data-driven. Adding the time dimension to 3D models helps teams see project schedules, spot potential conflicts, and manage resources better in real-time.
To fully benefit from 4D BIM, the industry needs to adopt new technology and rethink how teams work together. Shifting from traditional methods to better data-sharing and real-time decision-making will help construction teams unfold the full potential of 4D BIM.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for the Architecture and Structure discipline. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: BIM Levels and Stages of Development Explained.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is 4D Scheduling in BIM?
4D scheduling is a visual simulation of the construction process created by linking a 3D BIM model with the project schedule. It adds time as the fourth dimension, allowing teams to see how a project will progress.
2. What is LOD in BIM?
Level of Development (LOD) in BIM is a standard that specifies the level of detail and accuracy in a 3D model. It helps teams understand how much information a model contains at different stages of a project.
3. What is the purpose of 4D?
4D BIM helps planners create realistic schedules and improves communication between planning and execution. It reduces misunderstandings and ensures that the actual construction process aligns with the plan.
