The 3D modelling market is set to grow significantly, reaching $22.19 billion by 2032. This growth reflects its expanding role in industries like structural engineering.
3D modelling has changed how engineers design and construct buildings, bridges, and other structures. It allows them to create detailed digital models that improve accuracy, identify potential issues early, and enhance collaboration. By refining designs in the digital stage, engineers can save time and resources while ensuring better project outcomes.
In this article, you’ll learn how 3D models are used in structural engineering, their key benefits, and practical applications, especially in steel & concrete structures. In addition, you’ll explore common challenges in 3D modelling and how engineers overcome them to improve project efficiency.
What are 3D Models in Structural Engineering?

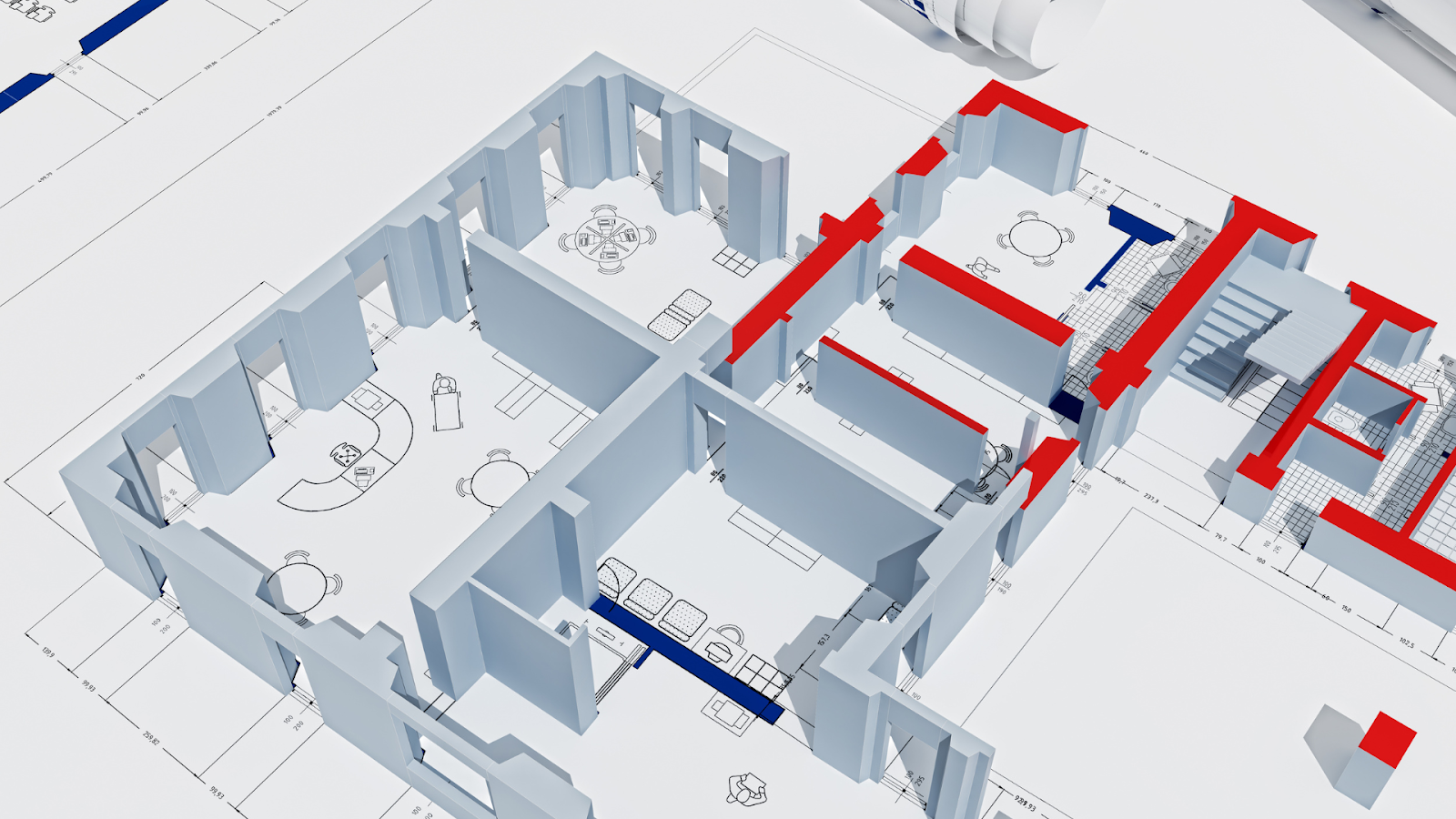
3D models are digital versions of buildings or infrastructure created with specialised software. They provide a clear, three-dimensional view of the structure, including its shape, materials, and key components such as beams, columns, foundations, and walls.
These models also include essential details such as material strength, properties, grade of material, load, calculations, and environmental effects. This helps engineers predict how the structure will perform in real-world conditions, making planning and construction more efficient.
By incorporating these critical details, 3D models provide a complete view of a structure’s performance and improve decision-making throughout the project.
Benefits of 3D Models in Structural Engineering
Accuracy and efficiency are crucial to a project’s success in structural engineering, and 3D modelling has significantly improved both. By creating precise digital representations of structures, engineers can identify potential issues early, reduce delays, and save valuable resources.
Beyond accuracy, 3D modelling also strengthens collaboration among project teams. A shared visual model improves communication, reduces misunderstandings, and ensures everyone stays aligned throughout the project.
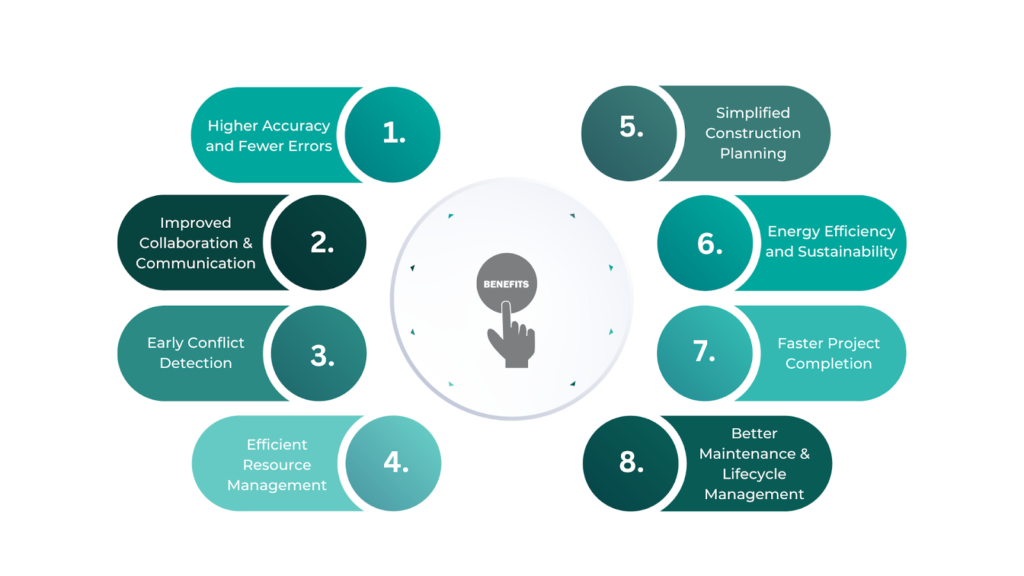
3D modelling is reshaping the construction industry by enabling:
Higher Accuracy and Fewer Errors
3D models can reduce mistakes in 2D plans with exact measurements, angles, and real-world data. Engineers can test different conditions, make quick changes, and ensure the design is accurate, reliable, and efficient.
Improved Collaboration and Communication
3D models provide a common workspace for architects, engineers, and contractors. Real-time updates ensure everyone is aligned, help reduce miscommunication, and speed up decision-making.
Early Conflict Detection
3D models help detect clashes before construction by integrating plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. Fixing these issues in the design phase prevents costly on-site modifications and safety risks.
Efficient Resource Management
Accurate models help estimate materials, reduce waste, and ensure efficient labour scheduling, leading to significant cost savings throughout the project.
Simplified Construction Planning
3D models allow contractors to simulate and plan construction sequences by identifying potential challenges in advance. This reduces delays and ensures smoother execution.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
3D models allow engineers to analyse environmental factors like sunlight, wind, and temperature to design energy-efficient structures, reducing long-term costs and environmental impact.
Faster Project Completion
3D models speed up construction timelines and ensure on-time project delivery by reducing errors, improving coordination, and enabling quick adjustments.
Better Maintenance and Lifecycle Management
Even after construction, 3D models serve as a reference for maintenance, renovations, and upgrades, ensuring long-term structural integrity and efficient facility management.
Beyond the construction phase, these models remain valuable tools for maintaining and improving structures over time. Their versatility makes them essential in various aspects of engineering and project management.
Also read: Understanding Concrete Frame Structures: Types & Components.
Applications of 3d Models in Structural Engineering
3D models play a crucial role in structural engineering by allowing engineers to create precise digital representations of buildings and infrastructure. These models go beyond simple visualisation by enabling engineers to assess structural performance and simplify construction processes.
From testing how a structure handles weight and pressure to planning construction and maintenance, 3D models are helpful at every stage of a project. In structural engineering, they help with:
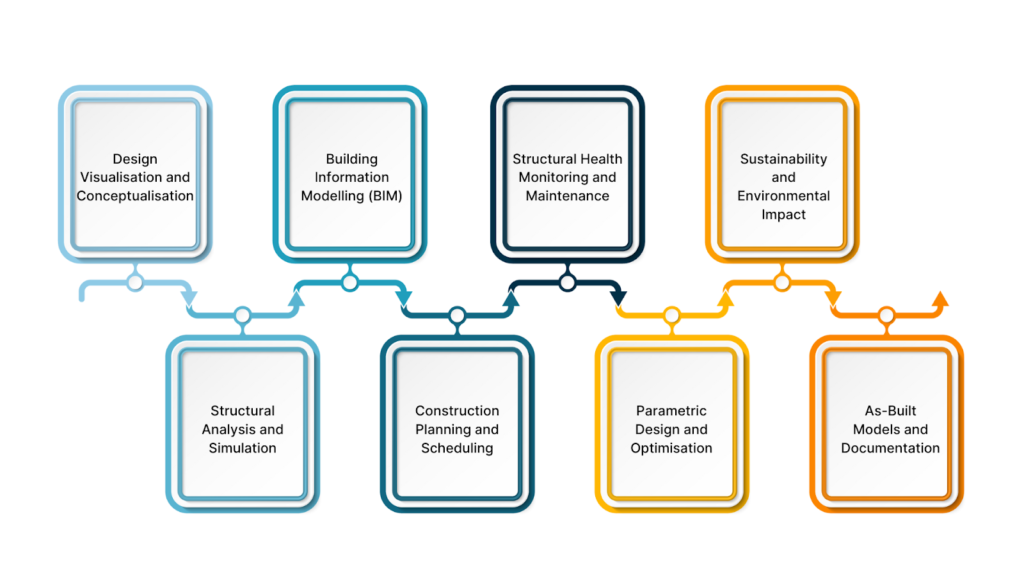
- Design Visualisation and Conceptualisation
3D models provide a realistic view of structures and make it easier for engineers, clients, and stakeholders to understand designs. This allows for:
- Better Visualisation: Clients and stakeholders can easily understand the design, especially for complex projects.
- Early Issue Detection: Engineers can identify clashes between structural elements and other building systems, reducing costly revisions.
- Structural Analysis and Simulation
3D models are integral in performing structural analysis and simulations. Engineers use 3D models to test how structures behave under different conditions, including:
- Load Distribution: Simulating the effects of weight, wind, earthquakes, and other forces ensures safety and efficiency.
- Effective Simulation: Studying vibrations and movement helps design stable structures, especially in high-risk areas.
- Building Information Modelling (BIM)
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is one of the most significant advancements in integrating 3D models in structural engineering. BIM expands 3D modelling by integrating data across design and construction processes, thereby improving:
- Collaboration: Architects, engineers, and contractors work from a shared digital model, which reduces errors.
- Clash Detection: BIM identifies conflicts, such as beams interfering with HVAC or plumbing, and allows corrections before construction.
- Lifecycle Management: Models track the entire lifespan of a building and help in maintenance and future renovations.
- Construction Planning and Scheduling
3D models also play a critical role in construction planning and scheduling. They improve construction efficiency by:
- Visualising the Construction Sequence: Engineers and contractors can organise resources, schedule labour, and plan equipment needs.
- 4D Simulation: Adding time-based data helps improve project timelines and identify potential delays.
- Structural Health Monitoring and Maintenance
Once a building or infrastructure is constructed, 3D models remain crucial in maintaining structural integrity over time. Engineers use 3D models for:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Sensors provide data on structural health, such as load capacity and crack formation.
- Planned Maintenance: Engineers can visualise and schedule repairs or upgrades without disrupting operations.
- Parametric Design and Optimisation
Parametric design is another important use of 3D modelling in structural engineering. In this process, engineers use algorithms and adjustable settings to shape the design. This helps create more efficient structures by:
- Upgrading Structural Components: Adjust parameters like material and shape to improve performance while reducing waste.
- Automating Design Adjustments: Changes in one part of the model automatically update related components and maintain structural integrity.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact
In the modern era of sustainable design, 3D models also help engineers create more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient structures. They allow engineers to:
- Analyse Environmental Effects: Simulate sunlight, airflow, and material efficiency to optimise energy use.
- Green Building Design: Help meet sustainability standards like LEED by improving natural lighting, ventilation, and material selection.
- As-Built Models and Documentation
After construction, 3D models are used to create as-built models of the finished structure. These models are essential for:
- Accurate Documentation: Provide a precise reference for future modifications or expansions.
- Asset Management: Help facility managers track performance, schedule inspections, and plan repairs efficiently.
Ready to simplify your projects and achieve these benefits?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Revit Architectural and Structural Solutions. They coordinate with your team to develop, record, and streamline the BIM Revit Model, along with the sheets, Bill of Quantities, Bill of Materials, and clash coordination.
3D modelling is crucial in various areas of structural engineering, but it is especially valuable in steel construction.
3D Modelling for Steel Structures
3D modelling for steel structures uses specialised software to create digital models of steel frameworks. These models include important components like beams, columns, braces, and connections, helping engineers design and analyse structures with precision.
3D modelling is essential in steel construction and helps make planning and execution more efficient. A 3D model of a steel structure consists of several key elements that define its overall design.
Below are the components of 3D modelling for steel structures:
| Components | Key Details |
| Structural Elements | Include beams, columns, trusses, plates, braces, and foundations, which are modelled with precise dimensions, material specifications, and connection details to ensure accuracy in design and construction. |
| Connections | Modelled based on joint types, such as welded or bolted, and material properties to ensure proper assembly and structural integrity. |
| Load Considerations | Include dead loads, live loads, wind loads, and seismic forces incorporated into the model to simulate structural behaviour under different conditions. |
| Material Properties | Steel’s strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance are integrated into the model to ensure compliance with performance and safety standards. |
| Fabrication Details | Well-detailed 3D models are directly translated into construction drawings, enabling manufacturers and fabricators to produce steel components precisely. |
| Clash Detection | Helps identify conflicts between structural and mechanical systems before construction, allowing for early modifications and preventing costly on-site issues. |
To create accurate and efficient steel structures, engineers rely on advanced 3D modelling techniques. These models simplify fabrication, detect clashes early, and improve overall project coordination. However, achieving these benefits depends on using the right tools.
Key Tools in 3D Modelling for Structural Engineering
3D modelling relies on powerful software tools that help engineers design, analyse, and improve structures precisely. These tools go beyond simple visualisation and assist in material selection, structural analysis, clash detection, and collaboration among project teams.
Each tool plays a crucial role in improving efficiency and accuracy in construction projects. Some of the key tools used in 3D modelling for structural engineering are as follows:
- Autodesk Revit
Revit is a leading tool for Building Information Modelling (BIM). It allows engineers to create, manage, and simulate building designs in both 2D and 3D. Its strong collaboration features make it essential for large-scale projects.
- Tekla Structures
Tekla is known for its advanced detailing and fabrication capabilities, particularly in steel and concrete construction. It allows a smooth transition from design to fabrication and helps reduce errors and improve efficiency.
- ETABS
ETABS specialises in building design and structural analysis. It integrates well with BIM tools and helps engineers assess a building’s strength and stability under various conditions.
- STAAD.Pro
STAAD.Pro is a versatile analysis and design tool that supports multiple materials, including steel, concrete, and wood. It is widely used for complex structures that require in-depth analysis.
- AutoCAD
AutoCAD is a trusted drafting tool used across engineering disciplines. While not a dedicated structural tool, it is essential for creating initial designs and works well alongside other modelling software.
- Rhino
Rhino is ideal for projects with complex, free-form geometries. It is widely used in architecture and engineering for non-standard designs, such as curved or highly detailed structures.
- SolidWorks
SolidWorks is a 3D CAD software that excels in precise modelling and simulation. It is especially useful for structural components that need detailed and accurate designs.
While these tools play a crucial role in simplifying the 3D modelling process, engineers often face challenges such as managing complex designs, ensuring model accuracy, and maintaining collaboration across teams.
Challenges and Solutions in 3D Modelling for Structural Engineering
3D modelling has made it easier for engineers to design, analyse, and build structures more accurately and efficiently. However, despite its many advantages, using 3D modelling in structural engineering also comes with its own challenges.
To fully benefit from 3D modelling, engineers must overcome these obstacles with the right strategies and tools. Below are some of the key challenges faced and their effective solutions that can help address these obstacles:
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Complexity in Modelling Large Structures | Break the structure into smaller, manageable sections to improve control and accuracy, and use parametric modelling tools to automate repetitive tasks. |
| Inaccurate Geometric Representation | Use advanced high-precision software like Autodesk Revit, conduct regular accuracy checks during modelling, and use digital twins for continuous monitoring. |
| Data Integration from Multiple Sources | Use BIM software to smoothly integrate different datasets while standardising formats for efficient data sharing and collaboration. |
| Clash Detection and Coordination Issues | Use clash detection tools like Solibri Model Checker within the modelling software and hold regular coordination meetings with stakeholders to resolve potential issues early. |
| Time-Consuming Rendering and Processing | Optimise the model by reducing unnecessary details for faster rendering and use cloud-based processing to handle computationally heavy tasks. |
| Software Compatibility and Updates | Ensure all team members use compatible software versions and maintain a continuous training program for updates and software changes. |
| Structural Loads and Material Properties | Use accurate material databases and load analysis features within the software while continuously updating and verifying material properties and load criteria. |
| Limited Collaboration and Communication | Use cloud-based modelling platforms for real-time collaboration while implementing version control and change tracking for better team communication. |
| Cost and Resource Management | Adopt project management tools to integrate cost analysis and resource allocation with the 3D model while monitoring real-time progress to keep the project within budget. |
| Model Scalability | Build scalable models using modular design approaches while regularly reviewing their scalability and efficiency, adjusting as the project changes. |
BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.

Conclusion
3D modelling helps engineers create digital versions of buildings and allow them to see the structure from all angles. This helps detect design flaws or weaknesses early by reducing errors before construction begins.
Looking ahead, technologies like AI, machine learning, and augmented reality will make 3D models even more advanced and interactive. Digital twins will offer real-time data, allowing engineers to predict maintenance needs and improve sustainability. These advancements will lead to stronger, more efficient, and eco-friendly buildings.
Are you looking for BIM solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for the Architecture and Structure discipline. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: A Guide to Creating Structural Revit Model in Design Development.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the structure of a 3D model?
A 3D model consists of corner points (vertices), connecting lines (edges), and flat surfaces (polygons). The vertices act as coordinates, the edges link them together, and the polygons create the outer surface of the object.
2. What is a structural analysis?
Structural analysis checks how a structure will handle different forces, such as weight, wind, and earthquakes. Engineers use it to ensure that buildings, bridges, and other structures are strong, stable, and safe.
3. What is structural 3D printing?
Structural 3D printing is a modern construction method where machines create and assemble building structures. It helps reduce manual work, lowers costs, and is a more efficient and environmentally friendly way to build.