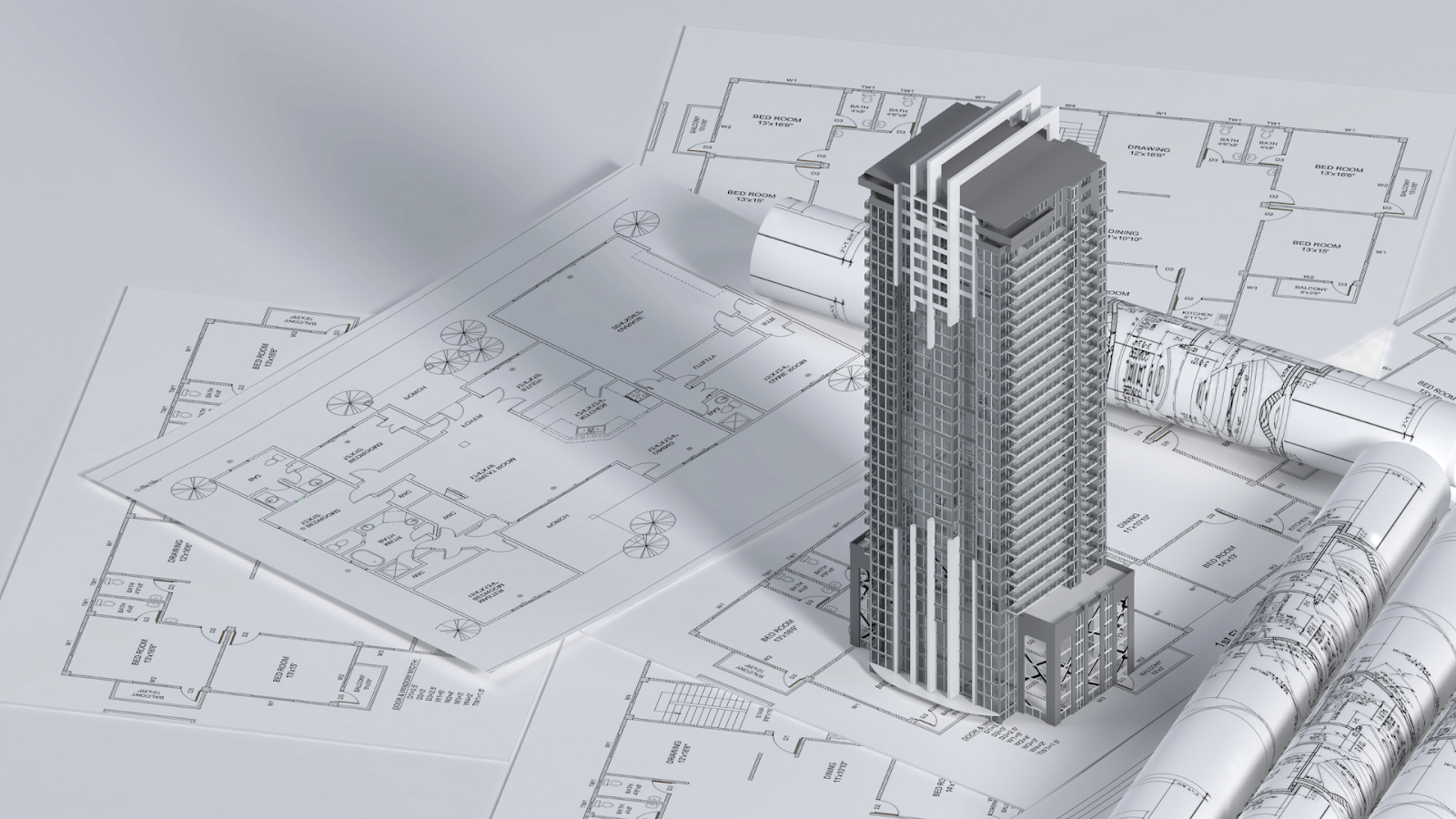
Research shows that 13.87% of people in the UK use Autodesk 3ds Max, highlighting its significant role in the design and visualisation industries. This powerful tool has become widely recognised in the architectural sector for creating detailed 3D models, objects, photorealistic & scenic renderings, and immersive visualisations.
Its versatility, and advanced features make it a top choice among architects, designers, and visualisation professionals. 3ds Max turns abstract concepts into compelling visual presentations by providing tools for precision modelling, dynamic lighting, and realistic texturing that convey design intent.
Whether you’re new to 3D modelling or looking to enhance your visualisation skills, this article will help you understand the fundamentals of 3ds Max. It covers everything from learning basic modelling techniques to creating stunning visualisations and tackling common challenges.
Understanding 3ds Max for Architecture

Autodesk 3ds Max is a powerful 3D modelling, rendering, and animation software widely used in architectural visualisation. It allows architects, designers, and visualisation experts to create detailed and photorealistic representations of projects, from small interior designs to large urban landscapes.
3ds Max manages large-scale projects and delivers photorealistic results, especially with rendering engines like V-Ray or Corona. Although it has a steeper learning curve than other tools, its flexibility and high-quality output make it an invaluable asset for professionals seeking top-tier visualisations.
Comparison of 3ds Max with Other 3D Modelling Software
Choosing the right 3D modelling software is essential for effective architectural design and visualisation. While 3ds Max is a powerful and versatile tool known for its advanced modelling features and realistic rendering, it’s helpful to compare it with other popular software options.
Below is a detailed comparison of 3ds Max and other top tools in the market:
| Software | Strengths | Limitations | Best for |
| 3ds Max | Advanced modelling and rendering toolsRich plugin ecosystemControl Polygons in any 3d Object and Model.Seamless integration with AutoCAD and Revit, Sketchup | Steeper learning curveResource-intensive | Architectural, Scene Creation, visualisation and high-detail modelling |
| SketchUp | Intuitive interfaceEasy for beginnersLarge model library | Limited rendering capabilities without pluginsLess suitable for complex, detailed models | Quick conceptual modelling and small-scale projects |
| Revit | BIM (Building Information Modelling) integrationPrecise architectural workflows | Limited rendering toolsLess flexible for artistic visualisations | Detailed architectural design, construction plans |
| Blender | Free and open-sourceStrong modelling and rendering toolsActive community support | Less industry-standard in architectureLimited interoperability with CAD software | Cost-effective visualisation, creative projects |
| Rhino + Grasshopper | Excellent for parametric and freeform modellingGreat for complex, organic shapes | Steeper learning curveLimited out-of-the-box rendering capabilities | Complex architectural forms, design experimentation |
While each software has unique strengths, 3ds Max is particularly suited for professionals who aim to create high-quality, photorealistic designs that effectively communicate their vision.
If you want to harness its full potential, you need to understand the specific features that make 3ds Max a standout choice for architectural design. The software handle projects of all scales and complexities, from precision modelling techniques to dynamic visualisation tools.
Also read: Autodesk Revit 2025: Features & Benefits: A Detailed Guide
Top 3ds Max Features for Architecture
3ds Max is more than just software; it’s a creative powerhouse for architects and designers. Whether you’re visualising a simple interior or a complex urban project, its robust features, intuitive tools, & seamless integration makes it valuable in architectural design.
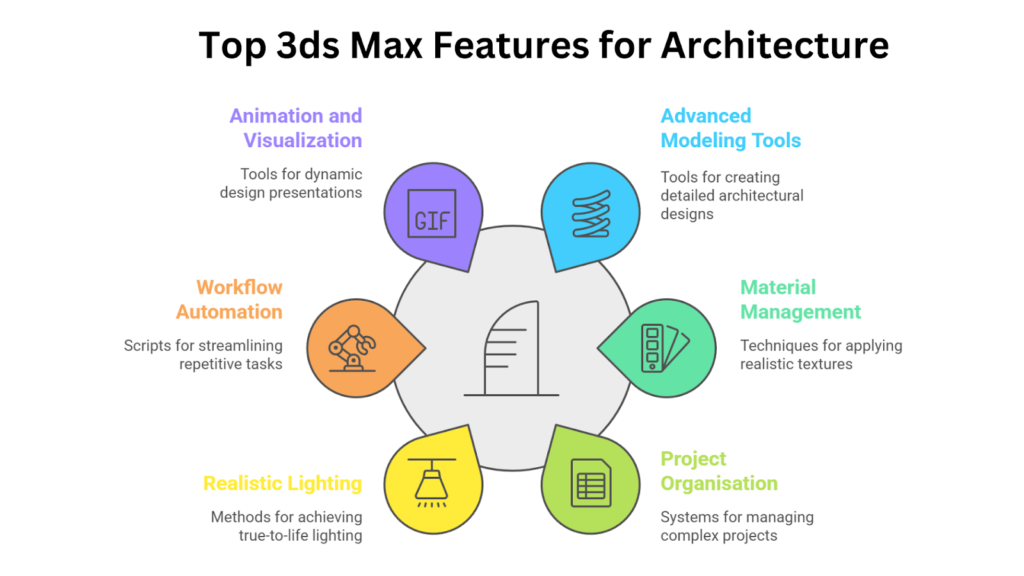
The features of 3ds Max that make it indispensable for architectural innovation include:
- Advanced Modeling Tools: 3ds Max provides versatile features for architectural needs that allow you to create everything from intricate interior details to large-scale urban layouts with precision.
- Material and Texture Management: 3ds Max enables you to create and apply realistic materials like polished wood, reflective glass, or textured stone.
- Simplify Project Organisation: The Scene Explorer helps organise complex projects by displaying objects hierarchically, allowing users to group, rename, and filter elements.
- Realistic Lighting and Rendering: Photometric lighting replicates real-world light fixtures, while global illumination and ray tracing enhance realism by delivering accurate shadows, reflections, and lighting effects.
- Automate and Customise Workflows: MAXScript automates repetitive tasks and customises workflows, helping to batch-apply materials, create parametric components, or clean up scenes.
- Animation and Visualisation: Camera tools enable cinematic effects such as depth of field and motion blur, while interactive walkthroughs and flythroughs offer immersive tours of your designs.
Harnessing these powerful features streamlines your workflow and drives exceptional results. At the core of these capabilities, 3D modelling uses essential techniques to transform architectural concepts into reality.
Basic 3D Modelling Techniques in 3ds Max
3ds Max provides several 3D modelling methods designed to suit different projects. Each method in 3ds Max is tailored to address specific design needs, offering flexibility and precision for a wide range of architectural projects.
Whether you’re working on creating basic structural forms, crafting intricate decorative details, or developing complex organic shapes, these methods provide the tools necessary to bring your vision to life.
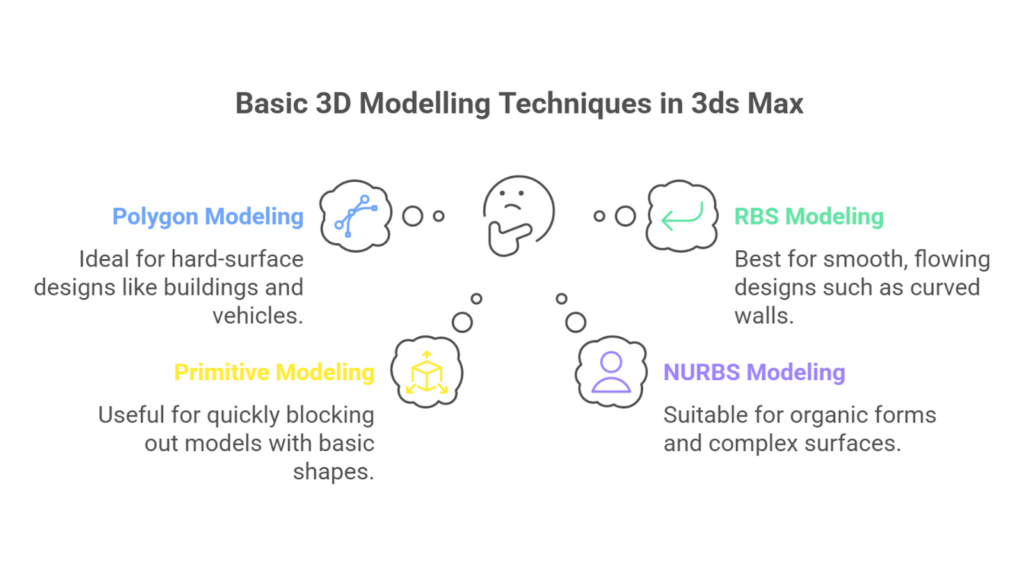
The four main modelling techniques commonly used in 3ds Max are:
- Polygon Modelling: Polygon modelling builds 3D objects by connecting vertices, edges, and faces to create a mesh. This versatile technique is commonly used for hard-surface designs like buildings, furniture, and vehicles and in architectural and interior designs.
- Rational Basis Spline (RBS) Modelling: RBS modelling uses splines (2D curves) defined by control points to create smooth, flowing designs. It’s ideal for shaping complex forms in lofting, extruding, or lathing and is commonly used for curved walls, railings, and ornamental architectural elements.
- Primitive Modelling: Primitive modelling uses basic shapes like boxes, spheres, and cylinders to create the foundation of 3D objects. It’s ideal for quickly blocking out models or building basic structures in the early design stages.
- Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines (NURBS) Modelling: NURBS modelling uses curves and control points to create smooth, precise surfaces. It’s ideal for organic forms, complex facades, and flowing architectural elements, offering high-quality models and flexible control for seamless design.
Understanding the core modelling methods in 3ds Max provides a foundation for creating various architectural elements. These methods come to life when applied to basic geometric forms, the building blocks of a design.
Creating Basic Geometric Forms for Architectural Purposes
Geometric forms are the foundation of architectural modelling in 3ds Max. These forms allow you to craft everything from simple layouts to intricate architectural masterpieces. They serve as the starting point for creating walls, floors, roofs, and other essential structures. The steps to create the basic geometry forms are:
| Steps | Key Details |
| Use Primitive Shapes | Go to the Create Panel on the right side of the screen.Under Geometry, choose either Standard Primitives or Extended Primitives.Click & drag in the viewport to create shapes like Box, Sphere, or Cylinder. |
| Position and Adjust | Use transformation tools:Move (W) to shift objects.Rotate (E) to adjust orientation.Scale (R) to resize objects. |
| Combine Primitives | Create multiple primitives, such as a cone and a cylinder.Use transformation tools to align and position the shapes.Apply a Boolean Modifier from the Modify Panel to combine or subtract objects. |
Following these steps allows you to craft geometric forms as the foundation for detailed and visually impactful architectural models. Once the creation phase is complete, the next step is modification.
Modifying Basic Geometric Forms for Architectural Purposes
While basic geometric forms provide the foundation for architectural models, their true potential is unfolded through modifications. The 3ds Max allows you to refine simple shapes into complex, functional structures. The steps to transform simple shapes into intricate components that align with your creative vision are as follows:
| Steps | Key Details |
| Convert to Editable Poly | Right-click on the object and select Convert to Editable Poly.Access sub-object levels (Vertex, Edge, Polygon, etc.) to modify geometry. |
| Extrude | Select a face or polygon and use the Extrude Tool from the Modify Panel.Pull a flat surface upward or outward to add depth. |
| Bevel | Combine extrusion with scaling to create slanted or tapered edges. |
| Inset | Shrink a polygon inward to create smaller, inner faces. |
| Cut Tool | Manually add edges or divide polygons for more detailed adjustments. |
| Use Modifiers | Go to the Modify Panel and apply Bend, Taper, or Twist tools.Use Boolean Operations to combine or subtract objects. |
With these modification techniques, you can transform basic geometric shapes into detailed and functional architectural elements. This flexibility allows you to adapt your models to the requirements of your project, ensuring both accuracy and creativity in your designs.
Refining geometric forms lays the foundation for architectural modelling, while visualisation brings your concepts to life and effectively communicates your vision.
Looking for 3ds Max-based solutions to elevate your designs?
BIM ASSOCIATES helps you with AR ready 3D-modeling for your objects, high poly, low poly 3d models, furniture, buildings, scenic renders, and landscapes and enables you to create scenic renders and videos.
3ds Max Tools for Visualisation in Architecture
3ds Max allows architects and designers to present their ideas in a realistic and engaging way. It provides powerful tools for creating photorealistic renderings and immersive scenes. The software offers a powerful Material Editor that enables users to design and manage materials with precision and control.
The key tools and techniques for applying materials, achieving realism, and optimising textures are:
| Aspect | Key Details |
| Using the Material Editor | Access the Slate Material Editor for node-based workflows or Compact Material Editor for simplicity.Apply textures like wood, concrete, glass, or metal by linking bitmaps to material slots. |
| Realism through Maps | Use Diffuse Maps for base colours and Bump Maps for surface irregularities.Utilise Reflection/Glossiness Maps for light interactions.Add depth with Normal Maps and Displacement Maps. |
You can fine-tune material properties like reflection, refraction, and glossiness to replicate real-world surfaces with precision. Leveraging procedural materials enables you to create scalable, seamless patterns ideal for elements such as bricks or tiles.
While crafting realistic materials and textures is crucial in architectural visualisation, proper lighting is just as important. Thoughtful lighting adds depth, mood, and authenticity, bringing your scenes to life.
Transforming Scenes with Proper Lighting in 3ds Max
Lighting is crucial for creating depth, mood, and realism in architectural visualisations. It enhances the overall aesthetics and highlights key design elements, guiding the viewer’s attention and bringing your scenes to life.
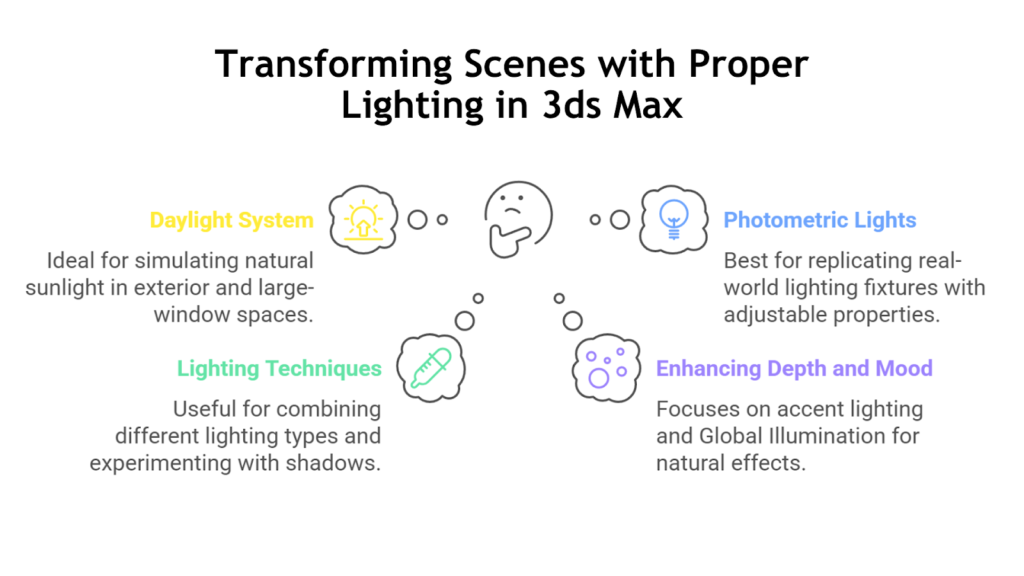
3ds Max provides versatile lighting tools designed for this purpose, such as:
- Daylight System: Simulate natural sunlight based on geographic location, date, and time—perfect for exteriors and spaces with large windows.
- Photometric Lights: Accurately replicate real-world lighting fixtures by adjusting intensity, colour temperature, and light distribution.
- Lighting Techniques: Combine ambient and direct lighting for balanced illumination, use IES Profiles for realistic light distribution, and experiment with shadow types, such as soft shadows, for added realism.
- Enhancing Depth and Mood: Highlight architectural features with accent lighting and use Global Illumination (GI) to create soft, natural light by simulating indirect light bounces.
These tools help bring architectural scenes to life, ensuring a professional and realistic presentation. Lighting adds depth and realism to your scenes, but the final step to achieving a polished and professional visualisation lies in optimising rendering settings.
Fine-tuning these settings ensures your images capture every detail, texture, and lighting effect with exceptional quality and precision.
Rendering Settings to Produce Finest Images
Rendering transforms your 3D models and scenes into stunning, high-quality visuals that showcase every detail of your architectural design. In 3ds Max, rendering settings are crucial for achieving the desired sharpness, lighting, and overall realism in your images.
The key rendering aspects to enhance your architectural visualisations include:
| Aspects | Key Details |
| Choosing a Renderer | Use built-in options like Arnold Renderer or third-party plugins like V-Ray and Corona Renderer for high-quality rendering capabilities. |
| Essential Settings | Higher resolutions (e.g., 1920×1080 or 4K) produce sharper images.Sampling improves the smoothness of lighting, shadows, and reflections.Anti-aliasing reduces jagged edges for a polished image. |
| Optimising Render Quality | Enable Global Illumination (GI) for realistic light bounces.Use Ambient Occlusion (AO) for subtle shadowing in corners and details.Adjust Exposure Controls to balance brightness and contrast. |
If you want to save time during the design process, test renders are performed at a lower quality for quicker iterations. Use the Batch Render Tool to manage and render multiple camera angles or lighting setups efficiently.
Optimising rendering settings ensure your designs are visually stunning, but a truly immersive visualisation goes beyond the final render. Simulating environments adds depth and context to your architectural scenes, bringing them to life with realistic foliage, weather, and atmospheric conditions.
Simulating Environments in 3ds Max Architecture
3ds Max offers tools to create natural elements like foliage, weather effects, and outdoor environments for architectural visualisations. You can use Standard Primitives or plugins like Forest Pack to generate trees, shrubs, and grass and adjust parameters like height, density, and variety for a natural look.
For weather effects, use particle systems to add fog, rain, or snow, and the Daylight System, along with volumetric effects, to simulate realistic lighting and depth.
Utilising Simulation Tools Such as Cloth and Wind to Enhance Realism
Simulating natural environments enhances context and depth in architectural scenes, but achieving dynamic realism goes beyond static elements. Simulation tools allow you to introduce lifelike motion and interactions, adding authenticity and visual appeal to your designs.
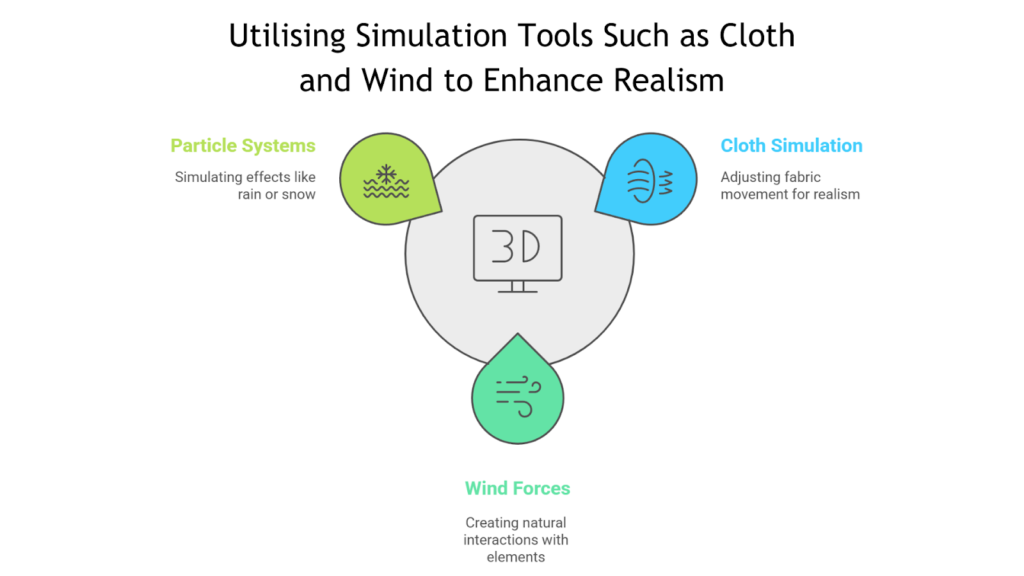
Key simulation tools in 3ds Max that help elevate realism and incorporate dynamic elements into your architectural scenes include:
| Feature | Key Details |
| Cloth Simulation | Use the Cloth Modifier for realistic fabric movement.Adjust settings like gravity, friction, and stiffness for desired effects. |
| Wind and Gravity | Add Wind Forces to interact with cloth, particles, or foliage.Simulate natural movements like rustling leaves or waving flags.Combine Wind and Gravity for dynamic interactions. |
| Particle Systems | Use tools like PArray or PF Source for effects like falling leaves, raindrops, or snow.Adjust the speed, direction, and lifespan of particles for accurate simulation. |
Once you incorporate these simulation tools into your workflow, you can add movement and authenticity to your architectural scenes, transforming static designs into dynamic, lifelike environments.
BIM Supports GREEN EARTH.

As you explore the full potential of 3ds Max for architectural visualisation, you may encounter challenges that can impact your workflow and productivity.
Common Challenges and Solutions in 3ds Max Architecture
Working with 3ds Max for architectural design opens up incredible possibilities, but like any powerful tool, it presents challenges. By understanding these challenges and applying practical solutions, you can navigate them with confidence.
The most common challenges faced when using 3ds Max for architectural design, along with practical solutions, are:
| Challenges | Solutions |
| Steep learning curve | Focus on primitives, interface, and simple modifiers.Use Autodesk Help Center or platforms like YouTube or Udemy.Work on elements individually and assemble them later.Join forums or social media groups. |
| Platform limitations | Use proxies for high-poly objects, group, and layer objects.Leverage plugins like Forest Pack (vegetation) and V-Ray (rendering).Use SketchUp or Blender for modelling and import into 3ds Max.Automate repetitive tasks with MAXScript. |
| Performance issues | Switch to Wireframe Mode and disable shadows.Ensure adequate RAM, GPU, and CPU.Use Region Rendering and adjust the quality of drafts.Delete unused objects and compact files.Keep software and plugins updated. |
Addressing these challenges with the suggested solutions optimises your workflow and allows you to fully leverage the capabilities of 3ds Max, ensuring a smoother and more productive architectural design process.
Conclusion
3ds Max is a powerful tool for beginners in architectural design, offering features for accurate modeling, realistic materials, dynamic lighting, and advanced rendering. Its ability to create detailed structures, simulate environments, and produce photorealistic visualisations makes it an essential asset for architects and designers.
Though mastering 3ds Max takes time and practice, regular use helps you open its full potential. Resources like tutorials and community forums allow you to overcome challenges and create effective architectural visualizations communicating your design concepts.
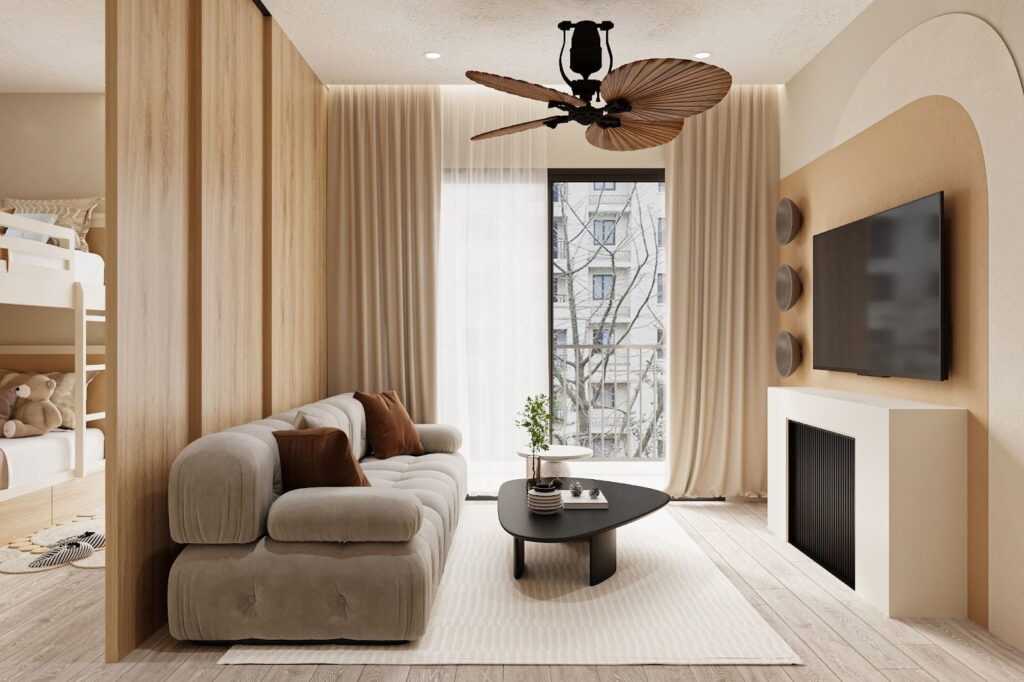

Interior Modeling, Texturing and Render with 3ds Max and Vray NXT. (Sample Image)
Are you looking for BIM Solutions?
BIM ASSOCIATES is your one-stop BIM Solution provider for Architecture and Structure. Their solutions help clients with better decision-making, cost-saving, efficient construction planning, and green earth initiatives.
You might also like: SD, DD, and CD Drawings Explained for Successful Construction.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What type of modelling is 3ds Max?
Autodesk 3Ds Max is professional 3D computer graphics software for creating 3D animations, models, games, and images. It is widely used in gaming, architecture, and film due to its advanced modelling and rendering capabilities.
2. Is 3ds Max better than Revit?
Revit is primarily designed for architectural design, building information modelling (BIM), and construction documentation, while 3ds Max excels in rendering and enhancing visualisation quality. Revit is ideal for creating precise architectural models, while 3ds Max is best for producing photorealistic renders and animations.
3. What are the three types of 3D models?
There are three types of 3D models:
- Solid Modelling: Used for engineering and CAD purposes, focusing on the object’s volume and structure.
- Wireframe Modelling: Represents the object’s edges and vertices, creating a skeletal framework.
- Surface Modelling: Creates a 3D surface, emphasising the object’s exterior details and curves.

